Safety Sensors & Switches
Overview Safety Sensors & Switches
September 26 2024 | Blog Post, Venus Automation
Have you ever considered what keeps the powerful machines in our factories and workshops from becoming hazardous? In an age where automation and robotics drive efficiency, the critical role of safety switches and sensors often goes unnoticed. These devices are more than mere components; they are the guardians of our workplaces, standing watch over both equipment and personnel.
Safety switches and sensors ensure that when something goes wrong, there’s an immediate response, minimizing the risk of injury and equipment damage. They operate quietly yet effectively, monitoring every movement and ensuring that each machine functions within safe parameters. Without them, the seamless operation of modern industrial processes would be at the mercy of human error and mechanical failure.
In this blog, we will explore the various types of safety switches, including Enabling Switches, Position/Limit Switches, and Foot Pedal Switches. We’ll also delve into the realm of Safety Non-Contact Sensors, focusing on Inductive Proximity Sensors, Magnetic Coded Sensors, RFID Coded Sensors, and Stainless Steel Electronic Safety Switches. Join us as we uncover how these devices are not just components but essential elements of a safe and efficient industrial ecosystem.
Recent Posts
Safety switches : an overview
Safety switches, also known as disconnect switches or residual current devices (RCDs), are essential components in electrical systems designed to protect people and property from electrical hazards such as electric shock and electrical fires. These devices are crucial for maintaining the safety and integrity of electrical installations across various applications, from residential settings to complex industrial environments.
Safety switches serve multiple purposes:
Fault Protection: They provide critical fault protection for motors and heavy machinery by monitoring electrical currents. If a fault is detected, such as a short circuit or an overload, the safety switch will automatically disconnect the power supply, preventing potential damage to equipment and reducing the risk of fire.
Disconnecting Means: Acting as a reliable disconnecting means for service entrances, safety switches enable safe maintenance and servicing of electrical systems. They allow technicians to isolate electrical circuits before performing repairs or inspections, ensuring a safe working environment.
Current Leakage Detection: Residual current devices (RCDs) specifically monitor the balance of electrical current between live and neutral wires. If an imbalance occurs, indicating potential leakage to the ground (which could lead to electric shock), the RCD will trip and disconnect the circuit within milliseconds.
Enhanced Safety Features: Many modern safety switches come equipped with additional safety features such as manual reset functions, test buttons, and indicator lights that signal operational status. These features enhance user safety and facilitate easier troubleshooting and maintenance.
Regulatory Compliance: Safety switches are often required by electrical codes and regulations to ensure safe electrical installations. Compliance with these standards not only protects individuals but also helps prevent costly damages and liabilities for businesses.
By integrating safety switches into electrical systems, industries can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and create a safer working environment for employees. Their versatility and reliability make them indispensable in protecting against electrical hazards and ensuring the smooth operation of machinery.
Types of Safety Switches
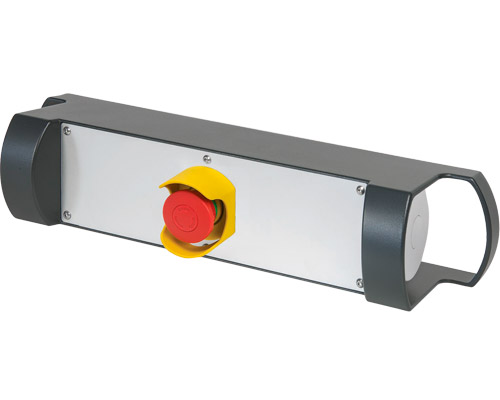
Enabling Switches
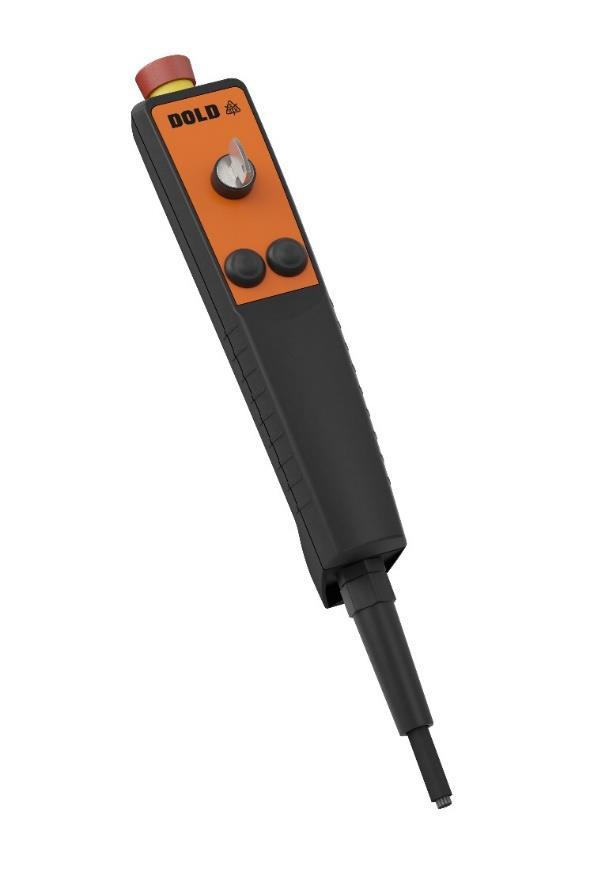
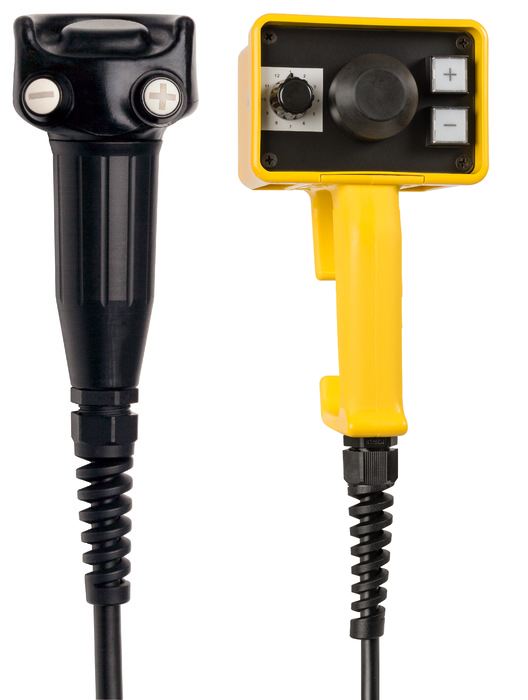
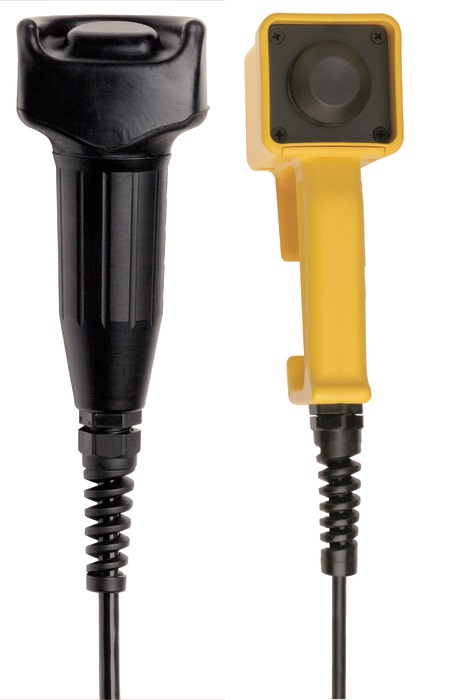
Enabling switches are critical safety devices designed to allow operators to control machines or processes in hazardous environments. These switches require continuous pressure to remain activated, offering a fail-safe solution if the operator releases the switch due to danger or discomfort. Often used in manual operation tasks like robot teaching or maintenance, enabling switches enhance safety by providing a controlled stop mechanism. They are typically three-position switches, offering multiple levels of control.
Pizzato’s FD Series Safety Limit/Position switches play a crucial role in automation, serving as reliable safety devices. These position switches, designed by Pizzato, are widely installed in industrial machinery worldwide. Their versatility allows them to adapt to various configurations, making them essential components for ensuring safety in automated systems.
With a focus on safety, the FD series of position switches is engineered to withstand challenging environments. Featuring a robust metal powder-coated body, these switches achieve a high level of protection with an IP67 rating when combined with compatible cable glands.
Pizzato’s FD Series Safety Limit/Position switches are indispensable safety devices that enhance automation systems, offering versatility, durability, and adherence to safety standards.

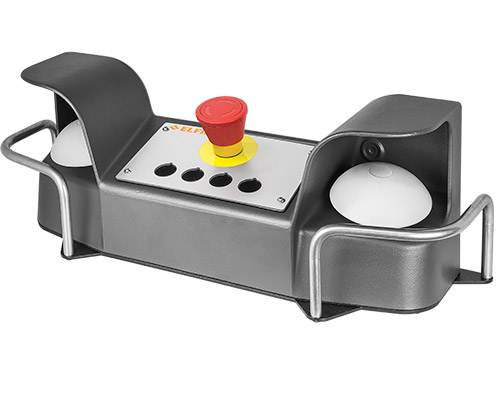
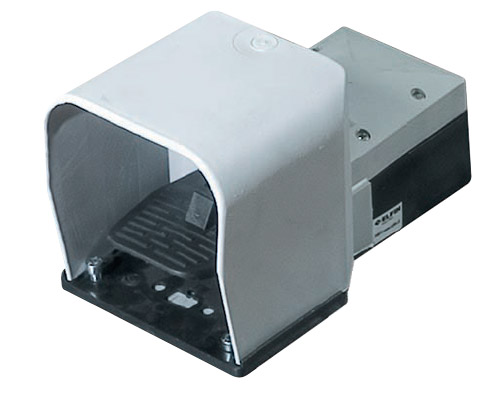
What is a Foot Switch?
A foot switch is a rugged electrical switch that can be activated by the simple application of foot pressure. It alters electrical contacts within a circuit when pressed. These switches are ideal for situations where hand-operated switches are inconvenient or pose safety risks. Their adaptability makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial needs.
Why are Foot Switches Essential?
Foot switches are an essential component in various industrial settings for several compelling reasons:
- Safety: In environments where operating machinery with hands could be risky, foot switches provide a safer alternative, allowing workers to maintain a safe distance.
- Convenience: These switches offer hands-free operation, which is useful when both hands are occupied, or when multitasking is required.
- Speed: Emergency stop foot switches allow quick interruption of power to machinery, improving response time and worker safety.
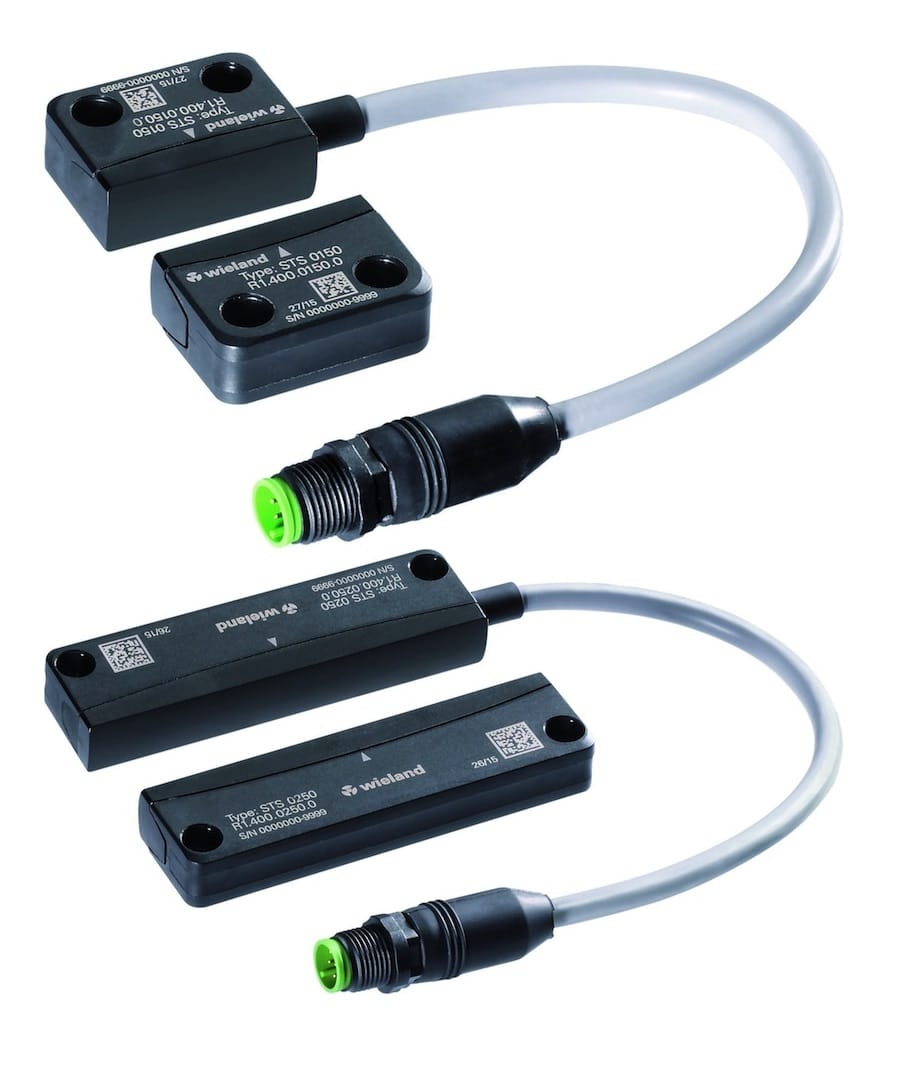
Safety Non-Contact Switches : an overview
Non-contact sensors detect objects, positions, and physical changes without direct interaction, ensuring enhanced durability and reducing the risk of mechanical wear. Operating on technologies such as capacitive, inductive, magnetic, optical, and RFID principles, these sensors are ideal for safety-critical environments where contact could cause contamination, wear, or inefficiency. They are commonly used in sectors like manufacturing, automation, food processing, and healthcare, offering reliable solutions for monitoring liquid levels, machine positions, object detection, and safeguarding hazardous areas. Their versatility supports safer, cleaner, and more efficient operational processes.
In industrial environments, non-contact safety sensors play a critical role in ensuring the protection of workers and equipment. They are frequently used in safety doors, emergency stop systems, and machinery safeguarding, preventing accidents by detecting when a person or object enters a hazardous zone. These sensors can also be integrated with control systems for automated responses, adding an additional layer of protection. Their resistance to contamination, vibration, and harsh conditions makes them ideal for long-term use in challenging environments
types of non-contact safety switches
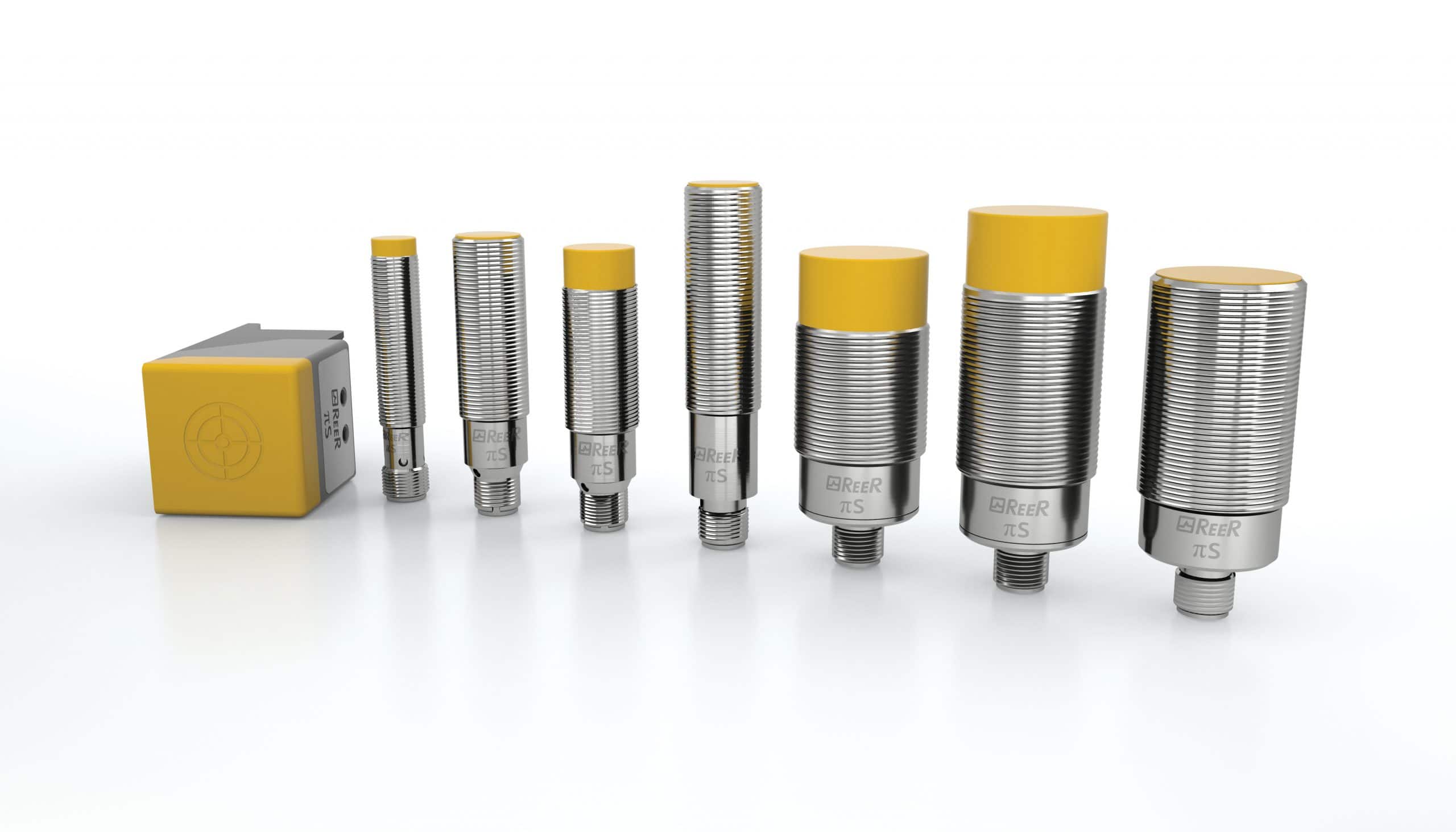
ReeR Safety Proximity Sensors – PI-Safe | Inductive Sensors
Boost Safety with PI-Safe Proximity Sensors: Certified and Reliable Proximity Sensors for Enhanced Safety.
The ReeR PI-Safe Inductive Proximity Sensor range increases the uptime and safety of your production through precision position detection to EN 60947-5-3 certification, ensuring operator and machine safety with in-built cross-fault monitoring. The PI-Safe Cylindrical Sensors come in M12, M18, and M30 sizing with both flush and non-flush mounting, with sensors for LED indication of power and signal status. Sensors are connected by M12 4-pole cables with up to IP69K protection ratings. The PI-Safe Square Sensors are 40 x 40 x 66mm with both flush and non-flush mounting variants and sensors for LED indication of power and signal status. Sensors are connected by M12 4-pole cables and are rated for SIL 3 – Ple.
PI-Safe Cylindrical Sensors
| Part Number | Material | Dimensions | Range | Operating Voltage | Safety Rating |
| PI M12 NF | Body: Stainless steel; Head: PBT | Non-flush M12 Thread 70mm length | 0.5-4mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M18 NF | Body: Stainless steel; Head: PBT | Non-flush M18 Thread 70.5mm length | 1-8mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M18 F | Body: Brass white bronze coated; Head: PBT | Flush M18 Thread 70mm length | 1-5mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M18 FR | Body: Brass white bronze coated; Head: PBT | Flush M18 Thread 86.5mm length | >10mm | 10-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M30 NF | Body: Stainless steel; Head: PBT | Non-flush M30 Thread 70mm length | 1-15mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M30 F | Body: Brass white bronze coated; Head: PBT | Flush M30 Thread 70mm length | 1-10mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 2, Pl d |
| PI M30 NF K | Body: Stainless steel; Head: PBT | Non-flush M30 Thread 80mm length | 6-12mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 3, Pl e |
| Part Number | Material | Dimensions | Range | Operating Voltage | Safety Rating |
| PI SQ F-NF | Body: Diecast zinc; Head: PPE | Flush or non-flush 40 x 40 x 66mm | 10-15mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 3, Pl e |
| PI SQ NF | Body: Diecast zinc; Head: PPE | Non-flush 40 x 40 x 66mm | 4-20mm | 19.2-30VDC | SIL 3, Pl e |

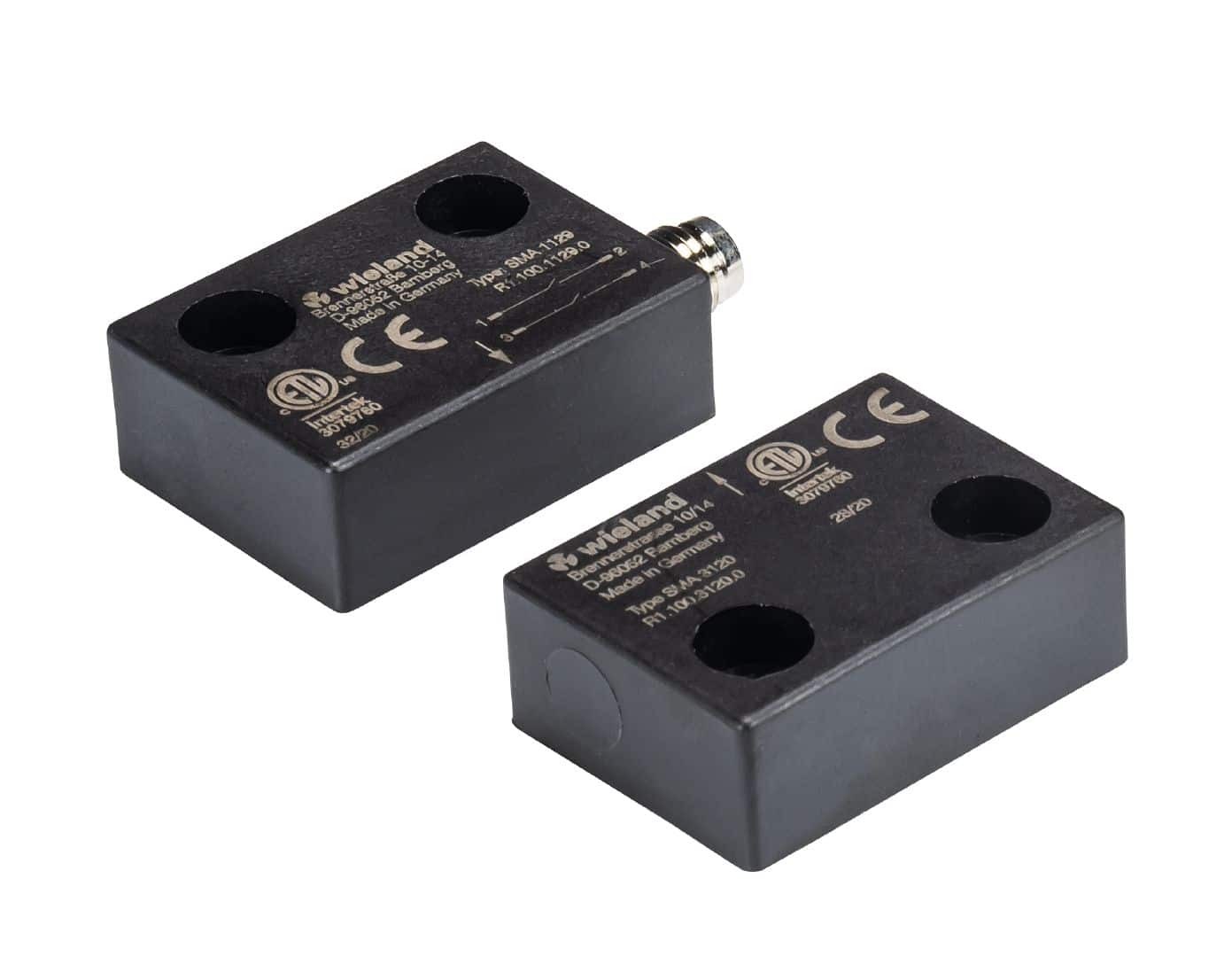
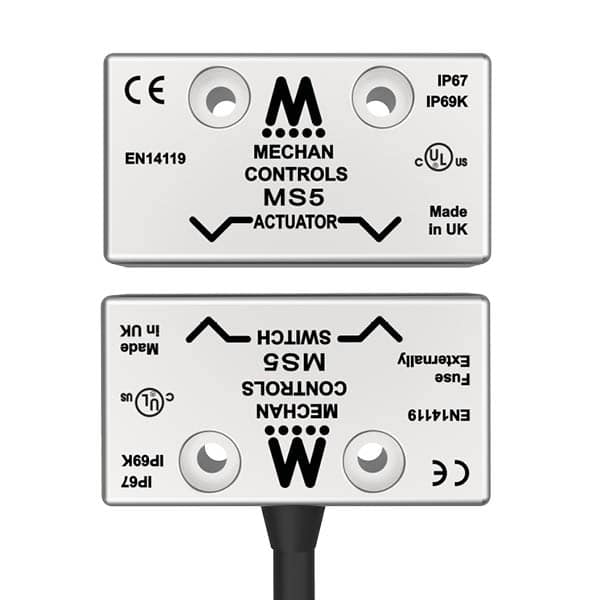
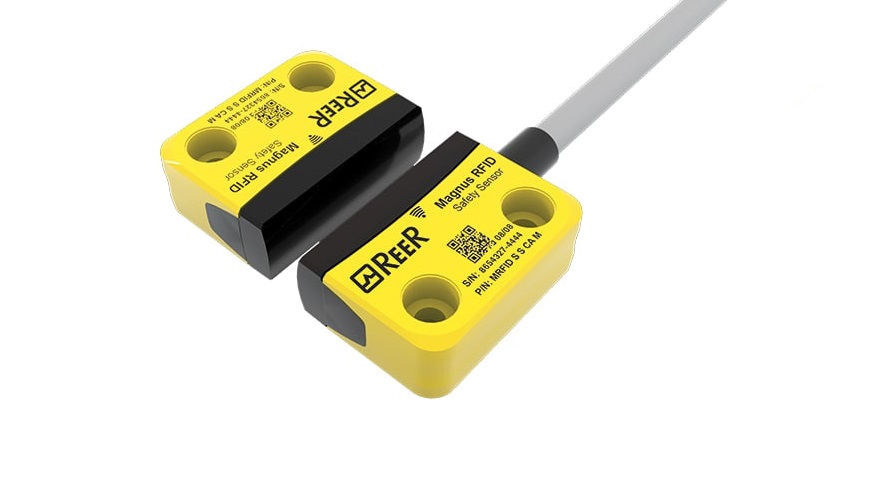
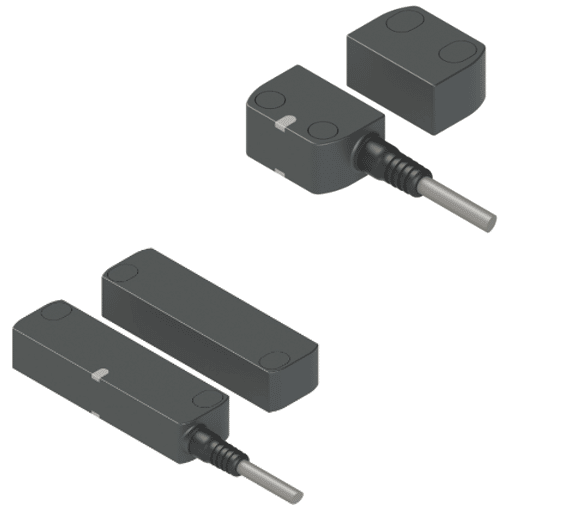
Magnetic Coded Safety Sensors: An Overview
Magnetic coded safety sensors are sophisticated devices designed to monitor the position of machinery, equipment, or access points in industrial settings. They employ a combination of magnetic fields and codes to ensure precise and fail-safe detection. The primary objective of these sensors is to prevent accidents, reduce downtime, and enhance overall workplace safety.
The Importance of Safety in Industry
Safety is a paramount concern in industrial environments. Accidents can lead to injuries, equipment damage, and costly production interruptions. Employing effective safety measures is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the well-being of personnel. Magnetic coded safety sensors play a crucial role in achieving these objectives.
How Magnetic Coded Safety Sensors Work
Magnetic coded safety sensors operate on a simple yet highly effective principle. They consist of two main components:
- Actuator: The actuator is typically attached to a movable part of the machinery or equipment, such as a gate or guard. It contains magnets and coded elements that emit a unique magnetic field pattern.
- Sensor: The sensor, mounted nearby, constantly monitors the magnetic field emitted by the actuator. When the actuator moves, the sensor detects changes in the magnetic field and interprets the coded pattern.
The sensor’s ability to recognize specific magnetic codes ensures high accuracy in detecting the position of the actuator. This technology provides an additional layer of safety by preventing unauthorized access, machine movement when it should be stationary, or unexpected equipment operation.
Applications of Magnetic Coded Safety Sensors
Magnetic coded safety sensors find applications in a wide range of industrial scenarios, including:
- Machine Guarding: They are used to monitor the status of guards, gates, or doors, ensuring that machinery remains safe to operate when needed and stops automatically when access is compromised.
- Conveyor Systems: Magnetic coded safety sensors are integrated into conveyor systems to control the flow of materials, guaranteeing the safety of workers and the efficient operation of the system.
- Material Handling: These sensors can be found in various material handling equipment to prevent accidents and improve efficiency.
- Access Control: Magnetic coded safety sensors are essential in restricting access to hazardous areas, ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter when it’s safe to do so.
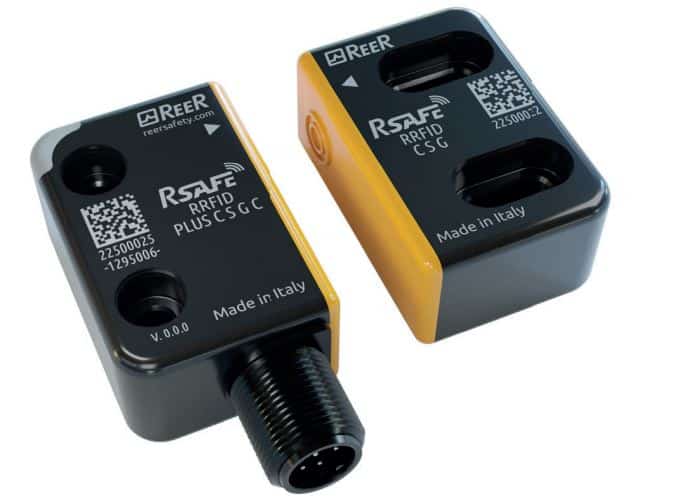
RFID Coded Safety Switches
RFID Safety Switches utilize RFID tags and readers to manage access control, real-time monitoring, and asset tracking. They play a crucial role in systems like Lockout-Tagout (LOTO) and emergency response, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with machinery. This adherence to safety standards, such as ISO 13849-1, is vital for workplace safety. These sensors provide real-time data for compliance and reporting, facilitating maintenance and repair tasks by offering valuable insights into equipment status and operational efficiency.
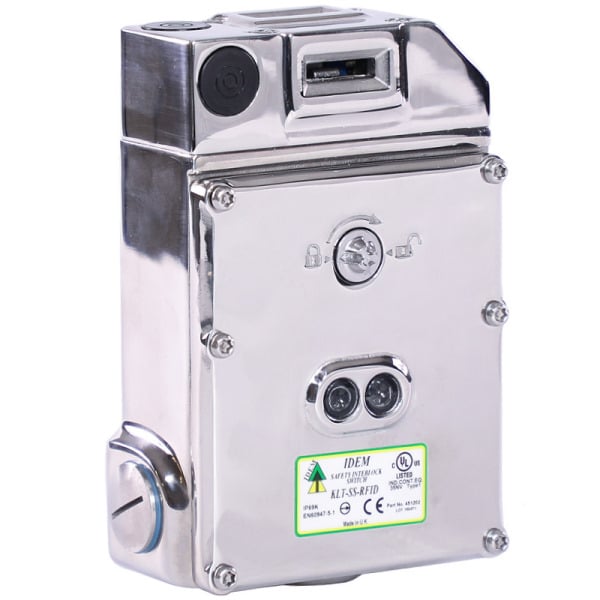
Stainless Steel Electronic
Stainless Steel Safety Devices are specifically engineered to comply with stringent food-grade standards, making them an excellent choice for the food industry, where minimizing contamination risks is paramount. These devices utilize high-quality stainless steel, which is inherently non-corrosive and resistant to the harsh conditions often found in food processing environments. This durability not only ensures longevity but also maintains the hygiene of the equipment.
The precise magnetically coded mechanisms employed in these devices enhance their functionality, ensuring reliable operation while safeguarding the integrity of food products. By effectively promoting safety and quality, these safety devices play a crucial role in food processing and packaging applications. They help ensure that machinery operates correctly and safely, preventing accidental openings and protecting both operators and products.
Moreover, the use of stainless steel aligns with modern hygiene practices, making cleaning and maintenance straightforward and efficient. As a result, Stainless Steel Safety Devices not only contribute to regulatory compliance but also foster a culture of safety and quality within food production facilities.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of modern automation, the importance of safety switches and sensors cannot be overstated. These devices are the unseen heroes, tirelessly working to protect our workforce and machinery. By understanding their significance, we can foster safer working environments that empower innovation without compromising safety. Your commitment to prioritizing safety is crucial in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape. Thank you for joining us on this exploration of essential safety technologies. Together, let’s continue to build a future where efficiency and safety go hand in hand.