24
What Are Safety Light Curtains?
Introduction to Safety Light Curtains
What are Safety Light Curtains & how do they work?
Safety light curtains operate by emitting invisible infrared beams across the protected area, between a transmitter and a receiver, sometimes with reflecting mirrors in between to alter the path. These beams form a detection grid—when uninterrupted, the system knows it is safe, and allows the machine to run. If any beam is broken, such as by a hand entering the area, the system instantly detects it and stops the machinery.
For example, in a press machine, safety light curtains are mounted at the front of the hazard zone. If an operator’s hand crosses the beams, the receiver will no longer detect the beams blocked by this hand, immediately triggering a stop. This non-contact protective solution is ideal for environments requiring frequent access to dangerous areas, helping maintain safety without disrupting operations.
Detection and Response Mechanism
When an object breaks the beam field, the receiver indicates this by cutting power to its’ two ‘OSSD’ outputs. This is then detected by the safety controller (whether safety PLC or safety relay), which then cuts power to the machine. This response typically occurs in milliseconds, which is critical for preventing injuries. As the safety controller will only allow operation if a “safe” signal is transmitted from the receiver, this makes the system fail-safe in the event of power loss to the light curtain.
In applications like robotic assembly, safety light curtains protect operators during manual interactions. Once the area is clear and beams are restored, the machine can safely restart. Advanced features like muting and blanking allow operators to configure the curtain to expect certain beams to be blocked at a given time, allowing for use with moving products or to increase ease of installation.
Key Qualities of Safety Light Curtains
Scanning Range
The scanning range defines the maximum allowable distance between the transmitter and receiver while maintaining effective detection. This is essential in larger machinery setups where access points span several metres. For instance, in automated storage or palletizing systems, a long scanning range ensures broad coverage without compromising safety. Choosing the correct range helps prevent blind spots and supports safe machine layout planning
Protective Field Height
This refers to the vertical coverage of the light curtain. A lower field height might be used for finger or hand detection, while higher fields are used for full-body detection in larger applications like robot cells or packaging lines. Selecting the right protective field height ensures all necessary areas are safeguarded, reducing the chance of accidental entry into hazardous zones.
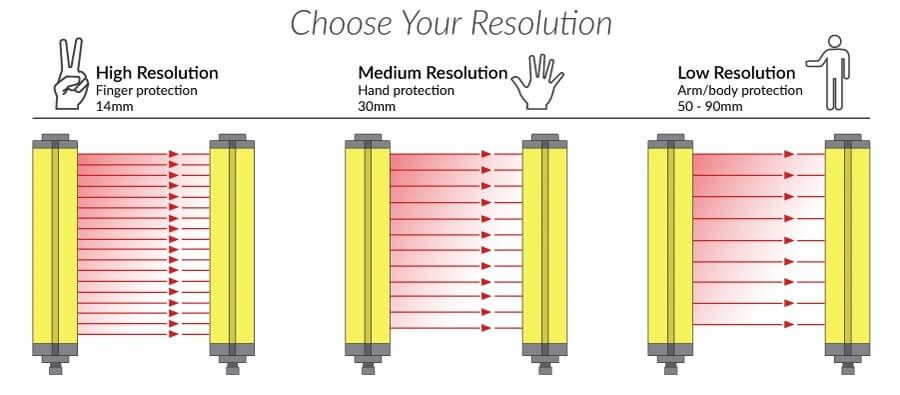
Resolution
Resolution is the distance between each beam. It determines the smallest object the curtain can detect. Common configurations include 14mm for fingers, 30mm for hands, and wider gaps for body detection. In precision settings, such as electronics manufacturing, high-resolution body detection are essential for detecting small tools or body parts entering danger zones.
Active vs Passive Systems
Active systems use separate transmitter and receiver units, while passive systems integrate both into one unit paired with a reflector. Active systems are ideal for wider spaces and critical applications, while passive systems work well in tight areas. Choosing between active and passive light curtains depends on layout, scanning distance, and installation flexibility.
The scanning range defines the maximum allowable distance between the transmitter and receiver while maintaining effective detection. This is essential in larger machinery setups where access points span several metres. For instance, in automated storage or palletizing systems, a long scanning range ensures broad coverage without compromising safety. Choosing the correct range helps prevent blind spots and supports safe machine layout planning
This refers to the vertical coverage of the light curtain. A lower field height might be used for finger or hand detection, while higher fields are used for full-body detection in larger applications like robot cells or packaging lines. Selecting the right protective field height ensures all necessary areas are safeguarded, reducing the chance of accidental entry into hazardous zones.
Essential Functions of Light Curtains
The Restart Interlock prevents machinery from automatically resuming after a safety breach. Instead, a manual reset is required once the area is cleared. This ensures that an operator has safely exited the hazard zone before operations continue. This is especially crucial for high-risk machines like injection moulders or presses, where unintended restarts could result in serious injury.
External Device Monitoring (also known simply as “feedback”) monitors the state of safety output devices such as relays, contactors and other actuators, to ensure that one or more of the components has not failed and become stuck in an unsafe (machine ON) position. If such a failure occurs, the EDM system will detect it and prevent the machine from reactivating, helping maintain the integrity of the safety circuit.
Muting allows materials to pass through the beam field under controlled conditions without stopping the machine. Sensors detect incoming objects (like pallets) and temporarily disable specific beams, allowing passage while protecting operators. This function is common in conveyor lines where safety and uninterrupted flow are both critical.
Blanking disables specific beams to allow stationary objects within the curtain’s path. Fixed blanking disables known beam positions, while floating blanking allows limited movement within a predefined range. It’s ideal in environments where fixtures or tools are permanently positioned inside the detection zone, such as in press brakes.
Beam Coding assigns a unique signal to each light curtain system, preventing interference when multiple curtains are installed close to one another. This ensures that only the correct receiver responds to its corresponding transmitter, reducing false triggers and downtime.
Benefits of Using Safety Light Curtains
Enhanced Safety Measures
Safety light curtains are essential in reducing the risk of injury in industrial environments. They create an invisible safety barrier that instantly commands a machine stop when a person or object enters a hazardous zone. Unlike traditional guards, they offer unrestricted access and higher flexibility, making them perfect for dynamic workflows in automation, robotic cells, or high-speed packaging lines. However, care must be taken to ensure that light curtains are placed at a sufficient distance to ensure that the machine is able to stop before whatever activated the light curtain reaches it (see “Understanding Response Time” below).
Prevention of Machinery Damage
Light curtains also protect machines by detecting obstructions early. If a tool, object, or limb enters the danger zone, the machine halts before impact, helping prevent equipment damage and costly repairs. This added layer of protection helps reduce unplanned maintenance and production delays.
Increased Operational Efficiency
By replacing bulky physical barriers with sensor-driven systems, light curtains improve access and speed up operations. Operators can interact with equipment more efficiently, and intelligent functions like muting and blanking help maintain productivity during material flow. This makes them ideal for applications where safety and speed must go hand-in-hand.
Choosing the Right Safety Light Curtain
Assessing Safety Levels
The selection process begins with evaluating the level of risk associated with the machine. Based on factors like injury severity and exposure frequency, machines are assigned safety integrity levels (SIL) or performance levels (PL). Higher-risk machines—like hydraulic presses—may require SIL 3 or PL e-rated safety light curtains to ensure compliance with international safety standards.
Determining Protected Height
The height of the light curtain must align with the area it needs to cover. For finger-level protection, a small height may be sufficient. For full-body detection at large entry points, taller curtains are necessary. Choosing the right height ensures complete coverage without leaving safety gaps.
Understanding Response Time
Response time is how quickly the curtain stops the machine after detecting a breach. Faster response times allow installation closer to the hazard, which is critical in space-constrained setups and high-speed lines. When calculating safe distances, always factor in both the machine’s stopping time and the curtain’s response time.
Evaluating Application Demands
Different environments have unique requirements. For dusty, wet, or outdoor applications, IP-rated rugged light curtains are essential. In clean, high-speed facilities, models with integrated muting or advanced diagnostics may be more appropriate. Understanding the application’s environment ensures optimal performance and long-term reliability.
Trends in Safety Light Curtains
Integration Improvements
Modern safety light curtains are designed for seamless integration with industrial control systems. With support for IO-Link Safety, PROFINET, and EtherCAT, they provide real-time diagnostics, faster wiring, and flexible configuration. This simplifies installations and enhances overall system intelligence—an essential feature for Industry 4.0-ready factories.
Enhanced Functionality
Today’s models go beyond simple stop functions. Many include built-in muting, alignment tools, diagnostic displays, and EDM. Some even support configurable detection zones, allowing partial access under certain conditions. These enhancements make light curtains more adaptable and efficient in fast-moving production environments.
Beyond Light Curtains – Safety Monitoring & Output Products
While selecting a robust safety input method is vital to any industrial safety system, equally critical is the ability to monitor and respond appropriately to those inputs. The safety monitoring and output range at Venus Automation provides tailored solutions to meet the needs of diverse machines and projects.
A key component in modern safety systems is the safety PLC. These programmable devices allow custom safety logic, with flexible input/output terminal assignments. Venus Automation offers a variety of models, including the MOSAIC PLC from ReeR, Samos PLC from Wieland, and GEMNIS PLC from Pizzato—each delivering advanced and reliable safety functionality.
Where complex programmability is unnecessary, alternative options such as safety relays are available. These include standalone relays, time-delay relays, speed-monitoring relays, standstill monitoring and timer relays, PCB relays and relay expansion modules. Also important are type-specific control relays, like the emergency stop relay, safety edge relay, light curtains relay, or two-hand control relay. These options provide effective and application-specific safety responses.
Regardless of input device or control relay, the emergency stop remains integral to any safety architecture, albeit not providing direct monitoring. To provide a complete solution, emergency stop accessories are also available, as well as emergency stop variants such as rope pull switches, and standard non safety-rated pushbuttons. Emergency stops are also sold integrated on other safety monitoring devices such as two-hand stations. Finally, Wireless safety systems, including wireless emergency stop units or remote controls and accessories, are also available.
Additional safety monitoring components include the safety encoder, which monitors motor speed, and interlock devices such as tongue solenoid interlock switch or electro-magnetic switches. For more complex safety guarding, multifunctional gatebox units provide a consolidated interface, easily mounted on protective enclosures, such as concertina guards.
Access restriction and control can also be achieved through electronic key systems, ensuring machinery operates only under authorized conditions. To connect chosen elements together, contact blocks are readily available. Finally, for output-side protection, safety contactors and pneumatic safety valve solutions are available to ensure reliable machine stoppage when hazardous conditions are detected.
Venus Light Curtain Offerings