Socket outlets, also known as power sockets or electrical outlets, are essential components in electrical installations, providing safe and reliable electrical connections for powering equipment.…
Socket outlets, also known as power sockets or electrical outlets, are essential components in electrical installations, providing safe and reliable electrical connections for powering equipment. In industrial environments, they serve as robust interfaces between fixed electrical circuits and portable devices or machinery. These outlets are engineered to handle higher current ratings and more demanding conditions than domestic sockets, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Industrial socket outlets often feature spring-loaded flaps or protective covers to prevent dust, water, or debris from entering the receptacle. Available in various pin configurations, including 3-pin, 4-pin, and 5-pin layouts, they enable multiphase plugs and distinct connector families to ensure compatibility with a wide range of equipment.
Common Use Cases in Industrial Settings
Socket outlets are used across a breadth of applications, offering reliable connection points in diverse industrial and commercial settings:
- Manufacturing floors: powering CNC machines, conveyors, and industrial robotics.
- Workshops: providing electricity for welders, drills, and grinders.
- Construction sites: supporting temporary power supply through switched socket outlets.
- Events and stage setups: using stage pin connectors or twist-locking connectors for lighting rigs and sound systems.
- Marine and mining: requiring IP66 or IP67 rated socket outlet designs for rugged, waterproof performance.
Standards and Safety Compliance (e.g., IEC 60309)
Most industrial socket outlets comply with IEC 60309 standards, ensuring consistent voltage ratings, colour-coded configurations, and safe operation. These outlets often integrate electrical interlocks or mechanical interlocks to prevent insertion or removal under load — avoiding damage to energized contacts or creating arcing hazards.
Adherence to international standards also allows for compatibility across brands, enabling users to select from a diversified range without compromising safety or performance.
Types of Socket Outlets
Panel Mounted Socket Outlets
Panel mounted socket outlets are fixed directly onto distribution panels or enclosures. These are ideal for switchboards and control panels where space-saving and secure connections are vital. Their robust housings and screw terminal designs offer ease of installation and serviceability.
Interlocked Socket Outlets
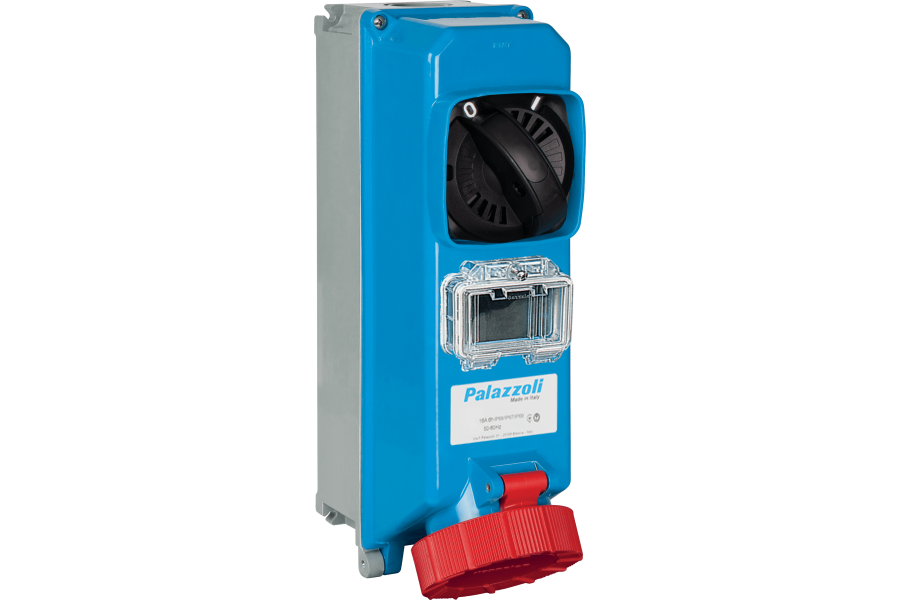
An interlocked socket outlet features a built-in switch mechanism that prevents the outlet from being energized unless a plug is fully inserted. These units enhance safety in industrial environments by ensuring proper electrical connection before power is applied. They are often used in conjunction with electrical interlock systems for increased protection.
Rotoswitched Socket Outlets
Rotoswitched outlets combine a rotary switch with a socket, allowing the user to manually disconnect power without removing the plug. Known for their rugged construction and reliability in harsh environments, these outlets are common in mining, marine, and heavy-duty industrial applications.
Wall Mounted Socket Outlets
Wall mounted units are fixed directly to surfaces and are widely used in both indoor and outdoor applications. With IP66 and IP67 ratings, they offer strong resistance to water and dust, making them suitable for exposed or weather-prone areas.
Switched & Socket Combinations
Combination switched socket outlets incorporate control switches and socket outlets into one unit, streamlining power distribution and safety control. These setups are frequently used in commercial applications, providing a practical and space-efficient solution.
Voltage, Current, and Phase Options
240V and 400V Socket Outlets
Socket outlets are available in a variety of voltage ratings, with 240V commonly used in single-phase applications and 400V for three-phase systems. These industrial power socket models are colour-coded according to IEC standards for quick identification and correct application.
16A, 32A, and 125A Models
Current ratings determine the load capacity of socket outlets. For instance:
- 16A for low-power machinery and tools.
- 32A for moderate industrial loads.
- 125A for high-power applications like large motors or HVAC systems.
Examples include the 32 A 5-pin socket and 50 A 5-pin socket — common across Australian socket outlets.
3-Pin, 4-Pin, and 5-Pin Configurations
These pin configurations support a range of electrical circuit types:
- 3-pin: live, neutral, and earth — ideal for basic connections.
- 4-pin: for three-phase without neutral.
- 5-pin: full three-phase with neutral and earth, including Australian 3-phase socket outlet setups.
Correct pin layout ensures safe current delivery and system compatibility.
Single-Phase vs Three-Phase Outlets
Single-phase outlets are used in general tools and light-duty equipment, while three-phase outlets provide consistent power for heavy-duty machines. Choosing between these options depends on your current requirements and the type of equipment involved.
IP Ratings and Environmental Resistance
IP66 and IP67 Rated Socket Outlets
Outlets with IP66 or IP67 ratings provide protection against dust ingress and strong water jets or immersion. These are essential for outdoor applications, ensuring uninterrupted operation in harsh environments.
Waterproof and Weatherproof Designs
Weatherproof socket outlets come with gaskets, seals, and durable housings to withstand exposure. Features like stainless steel screws and UV-resistant plastics enhance their lifespan and safety in industrial and commercial connectors.
Socket Outlets for Harsh Environments
Heavy-duty models are engineered with reinforced enclosures, enhanced degree of protection, and corrosion-resistant materials. They are suited to mining, marine, and remote construction sites — where conditions are demanding, and safety is paramount.
Technical Features and Installation
Mechanical Interlocks and Thermal Protection
Mechanical interlocks ensure that plugs cannot be inserted or removed while the outlet is energized. This prevents arcing and protects energized socket components. Some models also include thermal protection features to cut off power during overheating or overload scenarios.
Screw Terminals and Cable Entries
Reliable electrical connections are maintained through screw terminals and secure cable entry designs. This simplifies installation and ensures secure termination, especially in high-vibration or mobile environments.
Compatibility with Distribution Boards
Many panel and wall mounted socket outlets are designed for direct integration with industrial distribution boards, supporting streamlined electrical installations across manufacturing and logistics operations.
Safety Locking Mechanisms
Integrated safety locking mechanisms, including spring-loaded flaps and locking levers, prevent accidental disconnections and restrict access during maintenance — enhancing workplace safety and compliance.
Industrial Applications
Manufacturing Plants and Workshops
Industrial sockets are the backbone of power delivery in manufacturing facilities. They are used for equipment ranging from robotic arms to hydraulic presses, providing stable, high-current connections for 24/7 operations.
Construction and Temporary Power Setups
For temporary sites, switched socket outlets and combination units offer rapid deployment and safe power access. Their rugged designs and adaptable mounting options make them ideal for mobile generators and temporary boards.
Marine, Mining, and Outdoor Environments
These settings demand socket outlet features like corrosion resistance, watertight sealing, and enhanced mechanical strength. Resistant versions of industrial plugs and sockets with high IP ratings are vital to maintain safety and uptime in these unforgiving environments.
Choosing the Right Socket Outlet
Key Selection Criteria (Current, IP, Voltage)
When selecting a socket outlet, evaluate:
- Current rating (16A, 32A, 125A)
- Voltage rating (240V, 400V)
- Degree of protection (IP66, IP67)
- Pin configuration and electrical circuit type
Each of these factors should align with your electrical installation’s technical requirements and operational conditions.
Matching Outlets with Industrial Plugs
Industrial plugs and sockets must be matched in type, rating, and pin layout. Mismatched connections can result in faults or unsafe conditions.
Ensuring Long-Term Reliability and Safety
For reliable connection and safe operation over time, select outlets with quality construction, robust materials, and built-in interlocks. Look for models with features like stainless steel screws, spring-loaded covers, and clearly marked contact pins to support sustained performance in demanding applications.