25
Safety Switches: Everything You Need To Know
A Brief Overview of Safety Switches:
Safety switches are fundamental to industrial safety, preventing hazardous machine operations and ensuring compliance with workplace safety regulations. Designed to monitor and control access to dangerous areas, these switches act as critical fail-safe mechanisms that instantly halt machinery in case of an emergency. Solutions like Mechanical Interlock Switches provide a reliable means of preventing accidental machine activation, safeguarding personnel from moving parts. In high-risk environments, Plastic Body Mechanical Interlocks, such as the Wieland SMS Series, offer a lightweight yet durable safety solution.
For heavy-duty applications, Metal Body Interlocks like the Pizzato FG Series and Pizzato NG Series deliver robust protection, ensuring machinery remains inaccessible during maintenance or hazardous conditions. Additionally, in environments requiring corrosion-resistant solutions, Stainless Steel Mechanical Interlocks provide long-lasting reliability.
Beyond interlocks, other safety devices like Emergency Stops and Two-Hand Stations add further layers of safety, offering immediate shutoff capabilities when hazardous conditions arise. Implementing a comprehensive range of safety switches ensures a secure work environment while optimizing operational efficiency.
Ensuring safety in the industrial workplace is essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and fatalities. Effective safety measures not only protect employees but also enhance productivity by minimizing downtime due to accidents. Safety components, such as safety switches, play a critical role in enabling the safe operation of machinery, thereby creating a secure work environment. In industrial settings, safety switches play a critical role in protecting both personnel and equipment.
What are Safety Switches?
A safety switch is a device used to ensure the safe operation of electrical equipment by automatically disconnecting the power supply when an electrical fault or hazardous situation is detected. They are commonly used in industrial settings to protect both equipment and personnel from electrical accidents. Safety switches can be designed to detect a variety of conditions, such as ground faults, short circuits, or overloads. When such a condition is detected, the switch trips and cuts off the power, thereby preventing potential injuries or damage. They are essential components in maintaining compliance with safety standards and regulations in industrial environments.
Key Overview of Safety Switches:
PURPOSE AND FUNCTION
Safety switches are designed to quickly and reliably disconnect power to electrical equipment in the event of a fault or hazardous condition.
They protect personnel from electric shock and equipment from damage by interrupting the electrical supply.
TYPES
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Switches: Used to immediately halt machinery in an emergency.
Disconnect Switches: Allow safe isolation of electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency purposes.
Interlock Switches: Ensure machinery cannot operate unless protective guards or doors are in place.
Circuit Breakers with Safety Features: Provide overcurrent protection and disconnect in hazardous conditions.
APPLICATIONS
Widely used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants, to ensure machine and process safety.
Employed in electrical systems to prevent overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
Integrated into automated safety systems to monitor and control safety conditions.
COMPLIANCE AND STANDARDS
Safety switches help industries comply with safety regulations and standards such as OSHA, IEC, and ANSI.
They are essential for maintaining workplace safety and minimizing risks of accidents.
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
Installed at strategic points where there is a risk of electrical hazards or where quick disconnection of power is necessary.
Regular testing and maintenance are required to ensure they function correctly and meet safety standards.
FEATURES
Manual and Automatic Operation: Can be operated manually in case of emergencies or automatically in response to fault conditions.
Fail-Safe Design: Ensures that the switch will default to a safe state (disconnect power) if a fault occurs.
Durability: Built to withstand harsh industrial environments and frequent use.
INTEGRATION
Often integrated with other safety devices and systems, such as alarms, safety relays, and control systems, to create a comprehensive safety network.
Can be connected to monitoring systems for real-time diagnostics and remote monitoring.
Safety switches are designed to quickly and reliably disconnect power to electrical equipment in the event of a fault or hazardous condition.
They protect personnel from electric shock and equipment from damage by interrupting the electrical supply.
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Switches: Used to immediately halt machinery in an emergency.
Disconnect Switches: Allow safe isolation of electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency purposes.
Interlock Switches: Ensure machinery cannot operate unless protective guards or doors are in place.
Circuit Breakers with Safety Features: Provide overcurrent protection and disconnect in hazardous conditions.
Widely used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants, to ensure machine and process safety.
Employed in electrical systems to prevent overloads, short circuits, and ground faults.
Integrated into automated safety systems to monitor and control safety conditions.
Safety switches help industries comply with safety regulations and standards such as OSHA, IEC, and ANSI.
They are essential for maintaining workplace safety and minimizing risks of accidents.
Installed at strategic points where there is a risk of electrical hazards or where quick disconnection of power is necessary.
Regular testing and maintenance are required to ensure they function correctly and meet safety standards.
Manual and Automatic Operation: Can be operated manually in case of emergencies or automatically in response to fault conditions.
Fail-Safe Design: Ensures that the switch will default to a safe state (disconnect power) if a fault occurs.
Durability: Built to withstand harsh industrial environments and frequent use.
Often integrated with other safety devices and systems, such as alarms, safety relays, and control systems, to create a comprehensive safety network.
Can be connected to monitoring systems for real-time diagnostics and remote monitoring.
operational steps
The operation of safety switches involves several key steps to ensure electrical safety. First, there is continuous monitoring of electrical parameters or safety conditions, such as a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) constantly monitoring the current balance between the hot and neutral wires. Second, the system detects anomalies like current imbalance, excessive temperature, or unauthorized access to a dangerous area; for instance, an interlock switch can detect if a machine guard is opened. Third, the actuation step involves the switch mechanism disconnecting the electrical circuit, which could be a mechanical action, such as pressing an emergency stop (E-Stop), or an automatic response, like a circuit breaker tripping. Fourth, there is complete isolation of the electrical power to ensure safety, with the switch keeping the circuit open and the power cut off until the unsafe condition is resolved. Finally, the resetting step allows the safety switch to be reset manually or automatically to resume normal operation after addressing the unsafe condition; for manual switches, this often involves a physical action to reset the mechanism.
applications and functions
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Buttons: These switches are installed on machinery to allow operators to quickly stop the machine in an emergency.
Guard Interlock Switches: Used on machine guards and doors to ensure that machinery cannot operate unless the guard is closed, preventing access to dangerous parts.
Disconnect Switches: Allow for safe isolation of electrical circuits for maintenance or in the event of an emergency.
Circuit Breakers with Safety Features: Provide overcurrent protection and can also incorporate features to disconnect power in hazardous conditions.
Safety Relays: Monitor safety-critical processes and initiate shutdown procedures if unsafe conditions are detected.
Pressure and Temperature Switches: Trigger alarms or shut down equipment if pressure or temperature exceeds safe limits.
Explosion-Proof Safety Switches: Designed to operate safely in environments with explosive gases or dust.
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Buttons: These switches are installed on machinery to allow operators to quickly stop the machine in an emergency.
Guard Interlock Switches: Used on machine guards and doors to ensure that machinery cannot operate unless the guard is closed, preventing access to dangerous parts.
Disconnect Switches: Allow for safe isolation of electrical circuits for maintenance or in the event of an emergency.
Circuit Breakers with Safety Features: Provide overcurrent protection and can also incorporate features to disconnect power in hazardous conditions.
Safety Relays: Monitor safety-critical processes and initiate shutdown procedures if unsafe conditions are detected.
Pressure and Temperature Switches: Trigger alarms or shut down equipment if pressure or temperature exceeds safe limits.
Explosion-Proof Safety Switches: Designed to operate safely in environments with explosive gases or dust.
Safety switches serve several essential functions. First, they provide protection by preventing accidental startup of machinery during maintenance and interrupting electrical circuits in the event of a fault to prevent electric shocks and equipment damage. Second, they ensure compliance with industry safety standards and regulations, such as OSHA, IEC, and ANSI. Third, they facilitate automation integration by working with automated systems to enhance safety protocols, such as stopping a production line if an unsafe condition is detected. Lastly, safety switches offer monitoring and diagnostics by providing real-time monitoring of safety conditions and offering diagnostic data for maintenance and troubleshooting.
examples of different switches
Description: Manually operated switches designed to provide immediate cessation of machinery operations in emergencies.
Key Features: Large, red, mushroom-shaped button; easy to activate; typically latching, requiring manual reset.
Description: Switches that ensure machinery cannot operate unless safety guards or doors are properly closed.
Key Features: Mechanically or electronically linked to guards/doors; prevent operation if guards are open; used to protect access points.
Description: Switches that use magnetic, RFID, or other non-contact methods to monitor the position of guards or doors.
Key Features: Durable with no mechanical wear; tamper-resistant; suitable for frequent access areas and hygienic environments.
Description: Switches used to safely isolate electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency power cutoff.
Key Features: Handle-operated; can be locked in the off position; suitable for high-power applications.
Description: Switches that provide a continuous line of safety and can be activated by pulling a rope from any point along its length.
Key Features: Long coverage area; manual reset; robust design; used in conveyor systems.
Description: Manually operated switches designed to provide immediate cessation of machinery operations in emergencies.
Key Features: Large, red, mushroom-shaped button; easy to activate; typically latching, requiring manual reset.
Description: Switches that ensure machinery cannot operate unless safety guards or doors are properly closed.
Key Features: Mechanically or electronically linked to guards/doors; prevent operation if guards are open; used to protect access points.
Description: Switches that use magnetic, RFID, or other non-contact methods to monitor the position of guards or doors.
Key Features: Durable with no mechanical wear; tamper-resistant; suitable for frequent access areas and hygienic environments.
Description: Switches used to safely isolate electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency power cutoff.
Key Features: Handle-operated; can be locked in the off position; suitable for high-power applications.
Description: Switches that provide a continuous line of safety and can be activated by pulling a rope from any point along its length.
Key Features: Long coverage area; manual reset; robust design; used in conveyor systems.
offered products
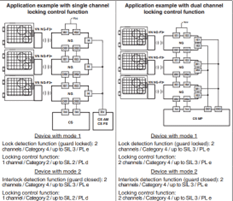
The NG series of safety locking switches are used on machines where the hazardous conditions remain for a while, even after the machine has been switched off, usually due to mechanical inertia of pulleys, saw disks, parts under pressure or with high temperatures. Thus, the switches can also be used if individual guards are only to be opened under certain conditions.

The ST – D and ST – H RFID safety sensors feature contactless actuation using advanced RFID technology and a digitally coded actuator. They offer high protection levels with IP67 and IP69K ratings and have a symmetrical housing that allows for universal fixing orientation. The sensors are equipped with multicolour signaling LEDs and are available in versions that can operate within an extended temperature range of -35 to +85 °C. Additionally, there are multitap versions with two or more actuators, and the ST H versions include an actuator with magnetic holding force.
From Detection to Action: Completing the Safety Chain with Outputs
While safety switches are essential for hazard detection and operator protection, they’re only one side of the equation. The safety monitoring and output range at Venus Automation provides tailored solutions to meet the needs of diverse machines and projects.
A key component in modern safety systems is the safety PLC. These programmable devices allow custom safety logic, with flexible input/output terminal assignments. Venus Automation offers a variety of models, including the MOSAIC PLC from Reer, Samos PLC from Wieland, and GEMNIS PLC from Pizzato—each delivering advanced and reliable safety functionality.
Where complex programmability is unnecessary, alternative options such as the safety relay range are available. This includes standalone relays, time-delay relay, speed-monitoring relay, standstill monitoring and timer, PCB relay, relay expansion modules, and control relays like the emergency stop relay, safety edge relay, light curtains relay, and two-hand control relay. These options provide effective and application-specific safety responses.
Essential manual inputs such as the emergency stop remain integral to any safety architecture, despite lacking an automatic safety input. Venus Automation supplies complete solutions including emergency stop accessories, pushbuttons, two-hand stops, and specialized devices like the rope pull emergency stop. For modern installations, wireless safety systems, including wireless emergency stop units, remote controls and accessories, are also available.
Critical integration elements such as contact blocks are supplied to ensure seamless circuit connections. Additional safety monitoring components include the safety encoder, which monitors motor speed, and interlock devices such as tongue solenoid interlock switch and electro-magnetic switches. For more complex safety guarding, multifunctional gatebox units provide a consolidated interface, easily mounted on protective enclosures like concertina guards.
Access restriction and control can also be achieved through electronic key systems, ensuring machinery operates only under authorized conditions. Finally, for output-side protection, safety contactors and pneumatic safety valve solutions are available to ensure reliable machine stoppage when hazardous conditions are detected.
Click to view our products