A CNC motor and control system forms the foundation of every modern machine tool, from compact CNC routers and 3D printers to high-performance CNC mills.…
A CNC motor and control system forms the foundation of every modern machine tool, from compact CNC routers and 3D printers to high-performance CNC mills. Together, the motor provides torque and motion while the control electronics manage accuracy, feedback, and trajectory. Whether driving a NEMA 23 stepper motor, a brushless servo, or a high-power industrial spindle, reliable servo drives, motion controllers, and regulated power supplies are essential for maintaining precision and productivity.
Understanding CNC Motor & Control Systems
Servo Motors and Stepper Motors
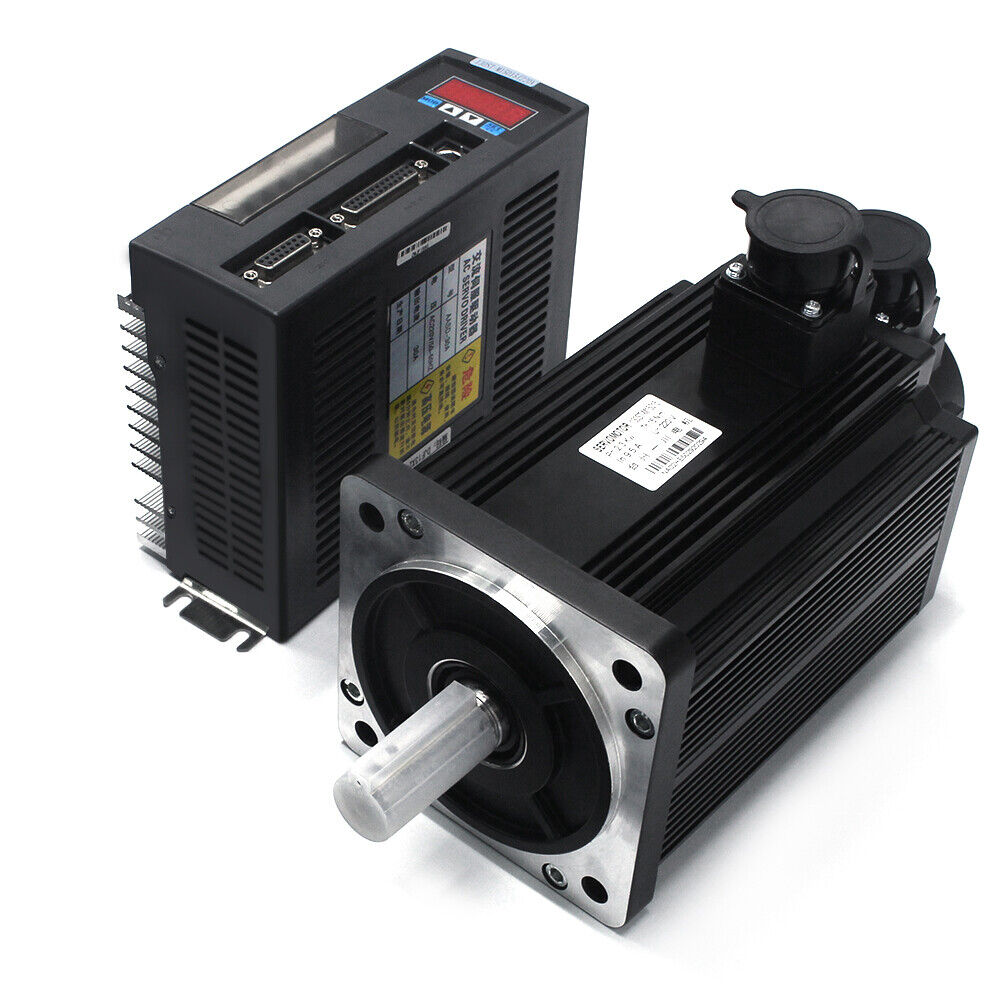
At the heart of every CNC system lies either a servo motor or a stepper motor. Servo motors operate with closed-loop control, continuously comparing feedback to commanded motion. Stepper motors, on the other hand, function in open-loop control and are common in lighter equipment such as 3D printers or desktop routers.
In industrial systems, AC brushless servos offer superior speed regulation, smoother torque delivery, and reduced maintenance compared to DC stepper configurations. For compact routers or prototype machines, NEMA 23 and NEMA 34 steppers remain popular choices due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of tuning.
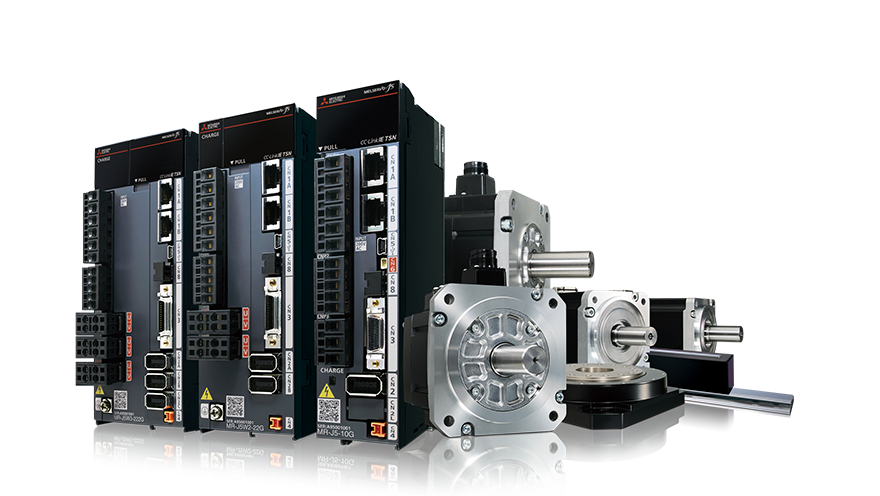
The Servo Drive and Motor Drivers
A servo drive (or CNC motor driver) converts control signals into precise current and voltage to power the motor. Advanced hybrid drivers can support both servo and stepper modes, enabling flexible integration across diverse machinery. The driver card or control card regulates power outputs, ensuring the correct current loop, velocity loop, and position loop operate simultaneously.
These control loops, managed through PID-based or adaptive control algorithms, stabilize torque and improve performance across varying loads — vital in CNC motion control systems.
Control System Architecture
The CNC control system serves as the command center. It interprets G-code, calculates toolpaths, and coordinates signals across axes via the motion controller. Modern CNC controls include real-time feedback analysis, trajectory correction, and synchronized multi-axis operation.
Typical configurations combine servo drives, limit switches, and electronic hand wheels for manual adjustment and setup. Enhanced safety is provided through emergency stop switches, spindle VFD outputs, and 24V DC power supplies that ensure safe and controlled power management.
Feedback, Sensors & Communication
A reliable feedback system is critical for maintaining accuracy. Devices such as encoders, position sensors, and tool length sensors return continuous digital signals to the controller. This feedback signal ensures that any positional error is immediately corrected, preserving machining precision.
In complex installations, feedback is transmitted through shielded Ethernet or fiber networks, while some smaller setups still use parallel port communication. Shielded cabling and grounding prevent interference, maintaining stable operation even near high-frequency power supplies.
Control Software & Motion Optimization
Advanced Motion Control
Control software drives the intelligence of CNC machines. It governs speed regulation, CNC motion control system synchronization, and S-curve trajectory planning to ensure smooth transitions between acceleration and deceleration.
High-end control platforms such as Centroid Acorn or Nighthawk CNC Controller support 4-axis motion, PC-less operation, and cloud connectivity, giving operators flexibility and efficiency. Many support LUA programming, V-carve CAM, and conversational programming to simplify setup for multi-axis machining or engraving tasks.
Safety & Reliability
Industrial reliability relies on robust safety circuits. A combination of emergency stop switches, limit switches, and protection mechanisms safeguard operators and prevent mechanical damage.
CNC motor and control panels often integrate diagnostic LEDs, digital displays, and fault logging to simplify troubleshooting. Reliable power supplies and cooling fans prevent thermal drift and ensure consistent performance over continuous operation.
Integration with Machine Tools
CNC systems today are not limited to traditional mills. They drive a wide array of machine tools including CNC routers, CNC laser engravers, CNC plasma cutters, and hybrid robotic systems.
The integration of servo motors, servo drives, and motion controllers enables adaptive torque response and precise positioning. In robotic applications, synchronized multi-axis motion ensures accuracy in welding, packaging, or pick-and-place automation.
CNC controls also connect seamlessly with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), forming part of a wider factory automation network. These systems communicate with sensors, actuators, and operator interfaces, ensuring coordinated operation across every production cell.
Energy & Power Management
Stable power delivery is critical for both stepper motor drivers and servo drives. The use of high-quality 24V DC power supplies and regulated AC-DC converters helps minimize noise and voltage drop.
For large installations, spindle VFD outputs and power outputs are isolated from signal electronics to prevent electromagnetic interference. Grounding and shielding are essential for both analog and digital control system reliability.
Some advanced drives even support Wireless Communication for monitoring load, fault states, and temperature in real time.
Software & Programming Features
Control Software
CNC control software translates CAD/CAM data into motion commands. Advanced suites support Cutter Compensation, Tool Length Compensation, and Probing Functions.
Features such as Electronic Hand Wheels, Multi-head Setups, and Probe Connections simplify manual adjustments and calibration. On-board memory (via Micro SD Card) and Ethernet connectivity streamline file transfers without external PCs.
CNC Kit Integration
Pre-configured CNC kits, such as 3-axis CNC kits or Stepper CNC kits, simplify retrofits for legacy machinery. Each includes CNC motor drivers, hybrid drivers, limit switches, and all required control wiring.
These kits are ideal for upgrading older CNC mills or routers, bringing them up to modern industrial automation standards with minimal downtime.
Conclusion
In every CNC motor control system, precision depends on seamless coordination between servo drives, motion controllers, and reliable power supplies. Whether building a custom CNC router, retrofitting a machine tool, or maintaining industrial automation equipment, integrating the right CNC motor and control components ensures accuracy, efficiency, and longevity.
Venus Automation provides complete CNC solutions — from servo motors and stepper motor drivers to control software, emergency stop systems, and factory automation integration — helping Australian industries achieve flawless motion and control.