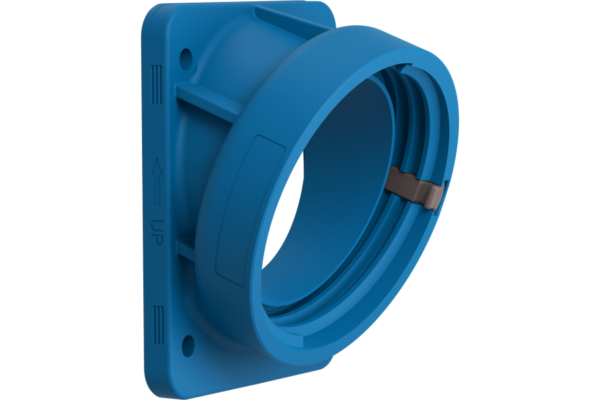
What Are Industrial Flanges?
Industrial flanges are mechanical components used to connect sections of piping, conduit, or equipment in both mechanical and electrical systems. In the context of electrical installations, they serve as secure connection points for cable glands, conduit fittings, and electrical enclosures. These flange connectors enable reliable power transmission and grounding in industrial environments, especially where electrical continuity and structural support are essential.
Role of Flanges in Electrical Installations
Flanges are commonly used in electrical wiring systems for mounting conduit entries and ensuring firm, vibration-resistant connections. In cable management systems, electrical conduit flanges provide a stable foundation for power distribution pathways. They are critical in maintaining proper alignment and shielding in switchgear, control cabinets, and heavy-duty equipment. In high-voltage or sensitive circuits, flanges also assist in isolating sections to prevent accidental disconnections and electrical faults.
Advantages of Using Flange Fittings in Electrical Systems
Using flange fittings provides several operational and safety advantages:
-
Simplifies installation of electrical enclosures and conduit systems
-
Enhances sealing and environmental protection (important for IP-rated assemblies)
-
Ensures better resistance to mechanical stress in harsh conditions
-
Supports standardized connector types and pin configurations
-
Reduces risk of electric shock through consistent earth connection paths
Types of Flanges Used in Electrical Applications
Electrical Conduit Flanges
Electrical conduit flanges act as termination points for conduit runs entering enclosures or panels. These are especially useful in surface mount or panel mount applications. They enable cable entry without compromising the enclosure’s integrity and often include screw terminals or gaskets for a sealed interface, compliant with industrial power socket standards.
Flange Couplings and Adapters
Flange couplings are used to connect two lengths of conduit or cable tray, ensuring mechanical and electrical continuity. Adapter flanges allow transitions between different conduit sizes or connector formats, supporting a wide variety of industrial connectors and maintaining voltage level compatibility.
Flange Mounting Solutions for Enclosures
These flanges are designed for installation on junction boxes, distribution boards, and electrical panels. Their compact design ensures they fit within tight spaces while supporting robust safety features, especially in high-current or multiphase applications. The mounting configurations are often tailored to standard bolt patterns and enclosure protection requirements.
Dielectric and Insulated Flanges
Dielectric flanges are essential in separating electrical currents between different sections of a system. They prevent galvanic corrosion and are used in areas where isolation between grounding systems is required — common in marine environments or advanced machinery setups. Insulated flanges are also key for maintaining system integrity during voltage variations or spikes.
Specifications and Standards
Common Flange Sizes and Dimensions
Flanges for electrical use typically follow standardized outer diameters and hole patterns. Sizes range from small conduit flanges for domestic sockets to large-diameter industrial flanges used with high-current equipment. Choosing the correct size is vital for proper fit, especially when aligning with connector types and enclosure layouts.
Material Options for Harsh Environments
To withstand harsh environments, industrial flanges are available in materials such as stainless steel, brass, aluminum, and reinforced polymer. Material housing must be selected based on factors like exposure to moisture, mechanical impact, or corrosive chemicals in construction sites or industrial machinery.
Industry Standards: ANSI, DIN, IEC Compliance
Most industrial flanges comply with global standards such as ANSI, DIN, or IEC. These standards define torque requirements, bolt spacing, and flange thickness, ensuring compatibility across equipment. Using compliant plug systems ensures safe operation and easy replacement in electrical setups.
Torque Requirements and Bolt Patterns
Proper flange installation requires adherence to specified torque values to ensure reliable connections without damaging gaskets or threads. Bolt patterns should match the flange’s pin configuration and support stable, high-performance connections across voltage ratings.
Applications of Electrical Flanges in Industrial Settings
Cable Management and Routing
Flanges help organize and secure cable entries in industrial wiring systems. In environments with multiple cable routes or control circuits, flanges assist in clean routing, preventing tangling and reducing wear on conductors.
Integration in Power Distribution Panels
Flanges are used in panel construction for connecting incoming and outgoing cables. They provide protection and strain relief for high-power connections, especially in three-phase systems or installations involving voltage converters.
Use in Control Cabinets and Switchgear
In automation systems, flange-mount connectors are crucial for integrating PLCs, safety relays, and other components into control enclosures. Their robust design supports both mechanical stability and thermal current management.
Marine, Mining, and Hazardous Location Use Cases
Dielectric flanges and corrosion-resistant variants are essential in marine and mining environments where electrical installations are exposed to water, vibration, and dust. These applications demand flanges with high ingress protection, secure earth connection, and resistance to voltage fluctuations.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Flange Mounting Techniques
Proper flange installation involves aligning bolt holes, applying the correct torque, and ensuring no stress is placed on attached conduit or wiring. Using compliant plug formats simplifies assembly and maintains environmental protection.
Gasket Selection and Sealing Methods
Choose gaskets that match the operating voltages, temperature range, and pressure ratings. High-quality sealing methods prevent moisture ingress and improve the degree of protection in electrical boxes and outdoor applications.
Preventing Electrical Shock and Ensuring Earth Connection
Ground pins and earth contact paths must be secured through properly torqued bolts and conductive flange materials. Flanges help prevent electric shock and maintain compliance with safety codes.
Maintenance for Long-Term Reliability
Inspect flange-mounted equipment regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or loose bolts. Reliable plugs and flanges reduce downtime and ensure consistent performance in both normal operation and emergency scenarios.
Choosing the Right Flange for Your Application
Matching Flanges with Connector Types
Selecting the correct flange involves matching it to the electrical connector’s shape, pin configuration, and current rating. For multipole connectors or heavy-duty plugs, robust flange housings are essential.
Voltage Ratings and Compatibility
Industrial flanges must support the system’s supply voltage without arcing or overheating. Flanges are categorized by maximum operating voltage and should be compatible with combinations of voltage seen in complex systems.
Current Ratings and Load Considerations
Depending on the current load, flanges should offer thermal current resistance and be paired with appropriate cable diameters. Overloaded flanges can fail under prolonged strain, making current rating a key specification.
Environmental Protection and IP Ratings
Ensure flanges have the right IP protection for the intended setting — particularly in outdoor, dusty, or high-moisture locations. Features such as rubber plugs, screw terminals, and sealing boots help maintain robust safety features even under harsh conditions.
Broader integration with Safety & Automation Systems
In modern industrial environments, flanges are only one part of an integrated safety architecture. These systems will work in tandem with various critical components such as safety PLCs, safety contactors or safety light curtains (including muting light curtains) to ensure real-time hazard detection and safe machine shutdown. Common peripheral safety devices like the emergency stop button, two hand station, and emergency stop rope pull are all effectively managed by the safety PLC’s logic structure.
Advanced installations frequently incorporate safety relays, safety non-contact switches, RFID switches, mechanical interlock switches, and solenoid locking switches—each adding specific protective functions to the machinery. To maintain continuous system health, engineers also deploy standstill monitors, speed monitors, soft starters, and reversing contactors within their automation frameworks. For measuring the product itself, solutions such as measurement light curtains can be integrated.
Beyond motion and logic safety, electrical condition monitoring is equally essential. Devices like insulation monitors, battery monitors, current monitors, voltage monitoring relays, phase sequence relays, under voltage relays, and undercurrent monitoring relays are often integrated to detect anomalies in power flow or equipment performance, with this data displayable on HMI Touch Panels or similar systems. To support reliable operation, high-quality power relays and regulated power supplies are essential.