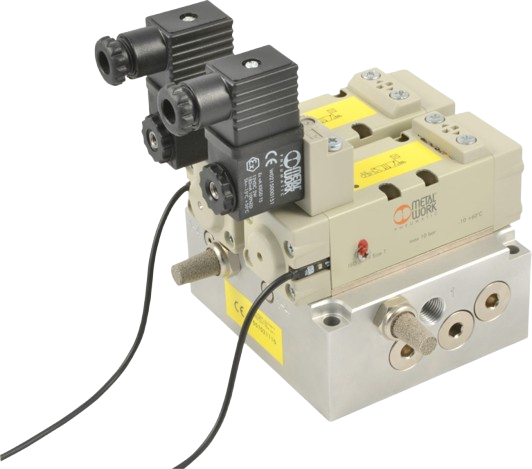
Safety Pneumatic Valves: Ensuring Precision and Reliability
Pneumatic safety valves play a vital role in protecting industrial systems from hazardous pressure build-up and system faults. Whether you require metal pneumatic valves for corrosive environments or safety shut-off valves to stop compressed air flow in emergencies, these components are critical to maintaining operational and personnel safety. Our category includes reliable solutions for high-performance applications across various industries.
Introduction
Overview of Pneumatic Safety Valves
Pneumatic safety valves are designed to automatically release or block compressed air in systems experiencing abnormal pressure conditions. These valves enhance equipment protection and operational reliability in systems using compressed air as a power medium.
Importance in Industrial Safety
In sectors like chemical processing, food manufacturing, packaging, and automotive, industrial pneumatic safety valves help prevent catastrophic failure. They ensure that compressed air safety valves or high-pressure pneumatic valves can react instantly to faults, thus minimizing damage and downtime. Their integration into emergency stop circuits also supports broader safety compliance strategies.
Broader integration with Safety & Automation Systems
In modern industrial environments, pneumatic safety valves are only one part of an integrated safety architecture. These systems will work in tandem with various critical components such as safety PLCs, safety contactors or safety light curtains (including muting light curtains) to ensure real-time hazard detection and safe machine shutdown. Common peripheral safety devices like the emergency stop button, two hand station, and emergency stop rope pull are all effectively managed by the safety PLC’s logic structure.
Advanced installations frequently incorporate safety relays, safety non-contact switches, RFID switches, mechanical interlock switches, and solenoid locking switches—each adding specific protective functions to the machinery. To maintain continuous system health, engineers also deploy standstill monitors, speed monitors, soft starters, and reversing contactors within their automation frameworks. For measuring the product itself, solutions such as measurement light curtains can be integrated.
Beyond motion and logic safety, electrical condition monitoring is equally essential. Devices like insulation monitors, battery monitors, current monitors, voltage monitoring relays, phase sequence relays, undervoltage relays, and undercurrent monitoring relays are often integrated to detect anomalies in power flow or equipment performance, with this data displayable on HMI Touch Panels or similar systems. To support reliable operation, high-quality power relays and regulated power supplies are essential.
Key Types of Pneumatic Valves
Metal Work Pneumatic Valves
Our range includes Metal Work Pneumatic Valves, known for their rugged stainless steel construction and precise control performance. These valves are widely used in food-grade, chemical, and hazardous environments, offering high durability, compatibility with ISO 13849, and options for redundant pneumatic valve systems. The design ensures reliable operation even in high-power load scenarios, supported by pneumatic valve actuators and position indicators for real-time feedback.
Safety Shut-off Valves
Safety shut-off valves automatically cut off the air supply when unsafe conditions are detected. Commonly used in high-current load applications or machinery with dual channel safety monitoring, these valves are critical in preventing accidental motion and pressurization. Their fail-safe operation, often paired with electropneumatic safety valves, supports total system lockdown when needed.
Essential Specifications and Features
Pressure Control Mechanisms
High-performance systems demand responsive pressure control mechanisms. Our pneumatic valves offer support for double-acting cylinders, fail-safe return, and dynamic load handling. This is essential for environments requiring fast response during pressure surges or component failure.
Material and Construction
All metal pneumatic valves in our range are made from corrosion-resistant stainless steel or treated alloys, ideal for harsh industrial environments. We also offer plastic housing options for lightweight or non-corrosive setups. These valves are designed for longevity and minimal wear, especially in high-use applications.
Maintenance and Ease of Use
Designed for easy installation, our pneumatic valves include modular components for faster servicing. Features like removable connection units, LED status indicators, and integrated displays reduce downtime and enhance safety monitoring. Many models support feedback capabilities and can be connected into broader control voltage branches.
Advancements in Valve Technology
Innovations Enhancing Safety
Recent innovations in pneumatic valve safety include real-time diagnostics, valve position feedback, and integration with PROFINET or other industrial protocols. These allow seamless incorporation into smart systems that require precise feedback circuits and minimal human intervention.
Emerging Trends in Valve Design
The shift toward energy-efficient, modular valve designs has led to new products optimized for lower energy costs and compact installations. Trends also include integrated mirror contacts for advanced system monitoring, ideal for applications demanding enhanced safety and automation.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Importance of Compliance
Compliance with international safety standards ensures not just safety but also operational legitimacy. Pneumatic valves used in safety systems must meet requirements such as ISO 13849, EN 574, or IEC 61508, depending on the application and region.
Key Certifications to Look For
Valves used in safety-related parts of control systems should be certified for SIL (Safety Integrity Level) or PL (Performance Level) ratings. Additional considerations include insulation voltage, thermal performance, and IP-rated enclosure protection for dust and water resistance.
Selecting the Right Valves
Factors to Consider
When selecting a pneumatic valve, consider switching voltage, holding force, environmental exposure (e.g., stainless steel vs. polymer housing), and integration with emergency stop systems. Also, assess compatibility with your existing control supply voltage and safety logic circuits.
Additional Considerations
Modern pneumatic safety valve systems are engineered not only for core safety functions but also to minimize machine downtime and improve operational continuity. The installation process has become increasingly streamlined, with reduced installation time thanks to modular designs and adaptable connector configurations that support a wide range of setups and industrial network protocols. This is particularly useful when integrating valves into systems with network connectivity for remote diagnostics and real-time status updates.
To enhance protection of process, safety valves are equipped to respond rapidly to a dangerous event or overpressure event, ensuring that critical failures are contained before damage spreads. Features such as precise valve position sensing, locking functionality, and functionality for guard locking further contribute to containment strategies in sensitive or hazardous zones. Additionally, durable designs ensure that disc lifts operate reliably across cycles without deterioration of the disc surface, even in high-load environments.
Pneumatic systems often depend on a stable incoming air supply, and proper integration of components like an OPCO gas pressure regulator or similar gas regulator ensures consistent flow and pressure control. Finally, enhanced performance measurement capabilities allow operators to assess system responsiveness, leakage, and actuation speed, supporting predictive maintenance and long-term system reliability.