
1
4 Facts You HAVE to Know About Wireless Safety Systems
A Brief Overview of Wireless Safety Systems:
WHAT ARE Wireless Safety systems?
Wireless systems can be categorized as a collection of wireless devices that work in uniform together to maximize security for people, property and other assets from any dangerous situation. Wireless systems can be simple as pressing a button to allow someone to enter a door without turning a physical key or on an industrial scale, remotely shutting down systems for any machinery because it started to operate in a dangerous manner without having to enter the danger zone and shut it down.
Wireless safety systems are revolutionizing industrial safety by eliminating cumbersome wiring while ensuring seamless emergency response and operator mobility. With advancements in technology, industries are rapidly adopting Wireless Safety solutions to enhance workplace protection and operational efficiency. These systems provide a flexible and reliable alternative to traditional safety mechanisms, enabling real-time safety control without physical constraints.
One of the most significant innovations in this field is Wireless Emergency Stops, which offer rapid response capabilities in hazardous situations. Unlike wired systems, these Contactless Emergency Stops provide instant shutoff from any location within the designated range, minimizing reaction time and potential risks. The advanced SAFEMASTER W Series further enhances safety with secure, interference-free communication, ensuring reliable machine stoppage when necessary.
For mobile and remote operations, E-Stop Remote Controls enable operators to trigger emergency shutdowns from a distance, offering unparalleled safety in dynamic work environments. As industries continue to embrace wireless safety solutions, these innovations are setting new standards for industrial protection, reducing installation complexity, and increasing workplace safety like never before.
Key overview of wireless safety systems:
PURPOSE AND FUNCTION
Ensure the safety of individuals and property by detecting and alerting to various hazards or security breaches through the use of wireless communication technologies.
TYPES
Motion Detectors: Alert you to movement in areas where it’s not expected.
Door/Window Contacts: Notify you if a door or window is opened.
Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Detect dangerous levels of smoke or gas and alert you.
Water Leak Detectors: Identify leaks that could lead to flooding or water damage.
APPLICATIONS
Workplace Safety: Systems for detecting gas leaks, monitoring for fire hazards, and ensuring overall safety compliance.
Asset Protection: Wireless surveillance and alarm systems to protect valuable equipment and inventory.
Employee Safety: Panic buttons or wearable devices for employees working in potentially hazardous environments or remote locations.
COMPLIANCE AND STANDARDS
Safety switches help industries comply with safety regulations and standards such as OSHA, IEC, and ANSI.
They are essential for maintaining workplace safety and minimizing risks of accidents.
INSTALLATION AND MAINTENANCE
Ideally installed at locations where there is a risk of a machine fault so any remote control can cut power to the machine.
Additional emergency stop and control functions can be implemented wirelessly for more safety.
Regular testing and maintenance are required to ensure they function correctly and meet safety standards.
FEATURES
Instant Alerts: Sends immediate notifications via audio alarms, SMS, emails, or app notifications to inform users of emergencies or system status.
Remote Monitoring: Allows users to receive alerts and monitor system status remotely through smartphones, tablets, or computers.
Communication Protocols: Utilizes technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks to connect sensors, alarms, and control panels without the need for extensive wiring.
Mesh Networking: In some systems, devices form a mesh network to extend coverage and reliability by relaying information between nodes.
Simple Setup: Typically easy to install with minimal wiring, often involving just mounting devices and pairing them with a central hub or control panel.
Scalability: Easily expandable to add more sensors or devices as needed without extensive reconfiguration.
Self-Testing: Periodically tests its own components and sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly and notifies users of any issues.
Diagnostic Tools: Provides troubleshooting and diagnostic information to help users identify and resolve problems.
Event Logs: Maintains logs of system events, alerts, and actions, which can be reviewed for troubleshooting or auditing purposes.
Usage Statistics: Provides data on system usage, including sensor activity and battery status.
Ensure the safety of individuals and property by detecting and alerting to various hazards or security breaches through the use of wireless communication technologies.
Motion Detectors: Alert you to movement in areas where it’s not expected.
Door/Window Contacts: Notify you if a door or window is opened.
Smoke and Carbon Monoxide Detectors: Detect dangerous levels of smoke or gas and alert you.
Water Leak Detectors: Identify leaks that could lead to flooding or water damage.
Workplace Safety: Systems for detecting gas leaks, monitoring for fire hazards, and ensuring overall safety compliance.
Asset Protection: Wireless surveillance and alarm systems to protect valuable equipment and inventory.
Employee Safety: Panic buttons or wearable devices for employees working in potentially hazardous environments or remote locations.
Safety switches help industries comply with safety regulations and standards such as OSHA, IEC, and ANSI.
They are essential for maintaining workplace safety and minimizing risks of accidents.
Ideally installed at locations where there is a risk of a machine fault so any remote control can cut power to the machine.
Additional emergency stop and control functions can be implemented wirelessly for more safety.
Regular testing and maintenance are required to ensure they function correctly and meet safety standards.
Instant Alerts: Sends immediate notifications via audio alarms, SMS, emails, or app notifications to inform users of emergencies or system status.
Remote Monitoring: Allows users to receive alerts and monitor system status remotely through smartphones, tablets, or computers.
Communication Protocols: Utilizes technologies such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, or cellular networks to connect sensors, alarms, and control panels without the need for extensive wiring.
Mesh Networking: In some systems, devices form a mesh network to extend coverage and reliability by relaying information between nodes.
Simple Setup: Typically easy to install with minimal wiring, often involving just mounting devices and pairing them with a central hub or control panel.
Scalability: Easily expandable to add more sensors or devices as needed without extensive reconfiguration.
Self-Testing: Periodically tests its own components and sensors to ensure they are functioning correctly and notifies users of any issues.
Diagnostic Tools: Provides troubleshooting and diagnostic information to help users identify and resolve problems.
Event Logs: Maintains logs of system events, alerts, and actions, which can be reviewed for troubleshooting or auditing purposes.
Usage Statistics: Provides data on system usage, including sensor activity and battery status.
operational steps
For most safety systems that are wireless, multiple components work together to form a single operating system. A wireless emergency stop system consists a radio controlled safety module and a wireless remote control. The safety modules feature three pairs of two-channel safety inputs, which can be used for devices like emergency stops, light curtains, or safety gates. They also include one safety output with three redundant contact paths. Additionally, each module offers eight inputs and outputs for user-defined control functions. For enhanced diagnostics, the modules are equipped with two status semiconductor outputs, an indicator output for signal reception quality, and a USB interface for comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. It receives signals from up to two hard-wired safety elements as well as signals from the active remote control via a secure transmission path. Safety-related switching commands are managed through relay outputs, while non-safety-related control signals are handled via semiconductor outputs.
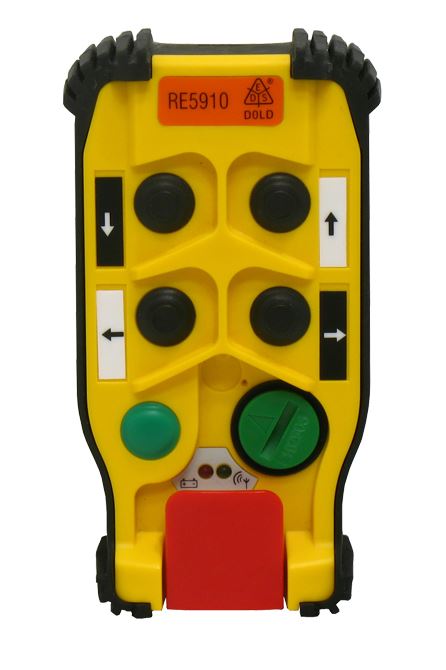
The wireless remote control is designed to be lightweight, ergonomic, and durable, making it easy to operate with one hand. It features a clear and intuitive control panel with buttons and switches that are safeguarded against accidental activation, such as from drops. Besides the emergency stop button, most remote controls contain a start button and four function keys, which can be configured as either single or double-position push-buttons, or as rotary switches with two or three positions, including options with automatic resetting. LED indicators display the settings or status of the remote control. In addition to a system identity code, the electronic key includes various settings (such as radio frequency or activity monitoring) and allows user privileges to be assigned to authorized operators.
examples of wireless safety systems
Description: A device that uses radio frequency (RF) communication to control relay switches wirelessly.
Key Features: Typically a standard safety relay that has additional wireless communication functionalities. Standard safety relay capabilities with the ability to provide electrical isolation between control signals and circuits being switched, thereby enhancing safety.
Description: It is designed to provide reliable monitoring and control for safety circuits.
Key Features: The radio remote control includes 1 emergency stop button, 1 start button, and 4 function buttons. It is designed to complement, rather than replace, conventional safety circuits. This means that while the remote control provides additional functionality, the wired safety circuits remain active and fully operational even when the remote control is in use.
Description: The electronic key enables the activation of the remote control and offers personal access permission to a certain configuration of the remote control.
Key Features: It contains the following information:
- Transmission Frequency: The radio frequency used for communication.
- System Identity Code: A unique code identifying the specific system.
- Activity Monitoring Interval: The time interval set for monitoring system activity.
Description: When not in use, the remote control should be placed in the charger and turned off. This action initiates the battery charging process.
Key Features: The charger has 2 monitoring contacts. These are used to detect the removal of the remote control.
Description: The receiver unit requires an aerial that can be mounted directly on the front of most radio controlled relay module.
Key Features: If the receiver is mounted in a metal enclosure the aerial has to be placed outside. For the outside mounting a special coaxial cable is available.
Description: A device that uses radio frequency (RF) communication to control relay switches wirelessly.
Key Features: Typically a standard safety relay that has additional wireless communication functionalities. Standard safety relay capabilities with the ability to provide electrical isolation between control signals and circuits being switched, thereby enhancing safety.
Description: It is designed to provide reliable monitoring and control for safety circuits.
Key Features: The radio remote control includes 1 emergency stop button, 1 start button, and 4 function buttons. It is designed to complement, rather than replace, conventional safety circuits. This means that while the remote control provides additional functionality, the wired safety circuits remain active and fully operational even when the remote control is in use.
Description: The electronic key enables the activation of the remote control and offers personal access permission to a certain configuration of the remote control.
Key Features: It contains the following information:
- Transmission Frequency: The radio frequency used for communication.
- System Identity Code: A unique code identifying the specific system.
- Activity Monitoring Interval: The time interval set for monitoring system activity.
Description: When not in use, the remote control should be placed in the charger and turned off. This action initiates the battery charging process.
Key Features: The charger has 2 monitoring contacts. These are used to detect the removal of the remote control.
Description: The receiver unit requires an aerial that can be mounted directly on the front of most radio controlled relay module.
Key Features: If the receiver is mounted in a metal enclosure the aerial has to be placed outside. For the outside mounting a special coaxial cable is available.
offered products
DOLD is an automation enterprise that specialises in industrial safety systems that includes their SAFEMASTER W line of wireless safety system. This catalogue of safety systems is designed to be flexible, reliable, maintenance-free, user-friendly and mobile when its operational meaning that customers can expect best security system to their machines for a safer work environment.
Here at Venus Automation, few of the SAFEMASTER W are available for customers to purchase. For example, Dold – BI 5910, an advanced wireless safety system designed to protect both people and machines. This system includes a wireless remote control that operators can carry into hazardous areas, allowing for immediate and accessible emergency stops. It features a safety transmission path that ensures reliable signal communication between the remote control and the radio-controlled safety module. Additionally, the system allows for the configuration of customized control functions that can be managed through the remote control. It also supports the integration of hard-wired safety components into the overall system.

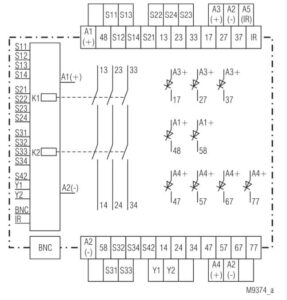
FUNCTIONALITY
The system includes a wireless remote control that operators can easily carry into hazardous areas. This feature allows for quick and safe emergency stops from locations where immediate access to control points is critical.
RELIABLE COMMUNICATION
It uses a safety transmission path to ensure secure and dependable communication between the remote control and the radio-controlled safety module, minimizing the risk of signal loss or interference.
CONFIGURATION
The BI 5910 allows for the configuration of control functions tailored to specific applications, which can be operated through the remote control. This flexibility enables the system to meet diverse operational requirements.
SYSTEM EXPANSION
The system supports the integration of traditional hard-wired safety components, allowing for a hybrid safety solution that combines wireless and wired technologies for comprehensive safety coverage.
STANDARDS
The BI 5910 is designed to meet high safety standards, ensuring that it provides reliable protection in compliance with relevant safety regulations.
APPLICATIONS
- Manufacturing: Enhances safety on production lines by allowing operators to quickly activate emergency stops or control machinery from a distance.
- Material Handling: Provides a means to control and monitor material handling equipment safely and efficiently.
- Heavy Machinery: Ideal for environments where operators need to manage large or complex machinery from remote locations
The system includes a wireless remote control that operators can easily carry into hazardous areas. This feature allows for quick and safe emergency stops from locations where immediate access to control points is critical.
It uses a safety transmission path to ensure secure and dependable communication between the remote control and the radio-controlled safety module, minimizing the risk of signal loss or interference.
The BI 5910 allows for the configuration of control functions tailored to specific applications, which can be operated through the remote control. This flexibility enables the system to meet diverse operational requirements.
The system supports the integration of traditional hard-wired safety components, allowing for a hybrid safety solution that combines wireless and wired technologies for comprehensive safety coverage.
The BI 5910 is designed to meet high safety standards, ensuring that it provides reliable protection in compliance with relevant safety regulations.
- Manufacturing: Enhances safety on production lines by allowing operators to quickly activate emergency stops or control machinery from a distance.
- Material Handling: Provides a means to control and monitor material handling equipment safely and efficiently.
- Heavy Machinery: Ideal for environments where operators need to manage large or complex machinery from remote locations

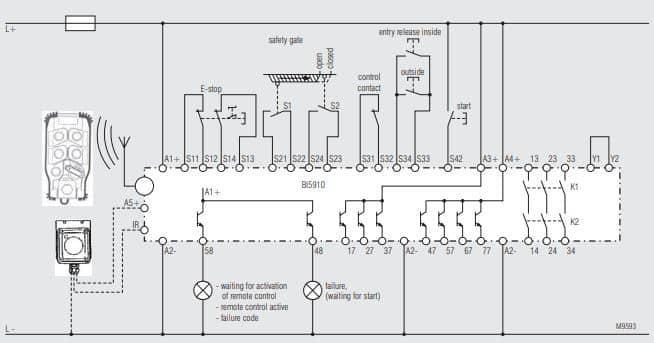
In addition to the BI 5910, DOLD RE 5910 is another crucial component that pairs perfectly with the BI 5910. The RE 5910 can be summarized as a wireless remote controller that can be taken by the operator into any dangerous zone and serve as a quick and reachable emergency stop. The Wireless Safety System is equipped with a secure transmission path that ensures reliable signal communication between the remote control and the radio-controlled safety module. Additionally, it allows for the customization of control functions tailored to specific applications, all of which can be managed via the remote control. The system also supports the integration of hard-wired safety components.
Wireless Control Is Only Half the Equation: Outputs Must Respond Reliably
Wireless safety systems like DOLD’s SAFEMASTER W provide unmatched flexibility in how emergency signals are triggered—but triggering a shutdown is only part of the safety equation. As such, safety input products form the foundation of a reliable safety architecture. Selecting the correct components to match specific hazards is essential for maintaining workplace safety.
Venus Automation offers a wide range of safety input devices to suit varied industrial applications. Detection solutions include the safety light curtain range, available for body protection, hand protection, and finger protection. Options supporting long range sensing and outdoor environments are available, along with muting light curtain models designed for automated processes. Supporting components such as photo cells, connection boxes, and muting accessories are also stocked. Additional detection options include multi beam systems and advanced laser scanner technologies.
To detect presence or motion at close range, proximity sensors are available, including non-contact switches, with magnetic, RFID, or stainless-steel technologies. Enclosures come in plastic, metal, or stainless-steel body variants for application-specific durability.
Mechanical safety detection is supported by products such as safety edge and mounting systems, contact mats, and bumpers with relevant edge accessories. These are ideal for perimeter and surface-triggered protection zones. For advanced zone control, trapped key systems and blocking devices ensure process integrity.
Manual control inputs are also critical in many safety scenarios. Venus Automation provides safety enabling switches, limit switch options, foot pedal switches, control pads, and standard control components.
Together, these input systems interface with the machine’s transmission system, ensuring rapid response to unsafe conditions. Combined with suitable outputs and logic control, they serve as the first line of defence in safeguarding personnel and equipment.
Click to view our products

