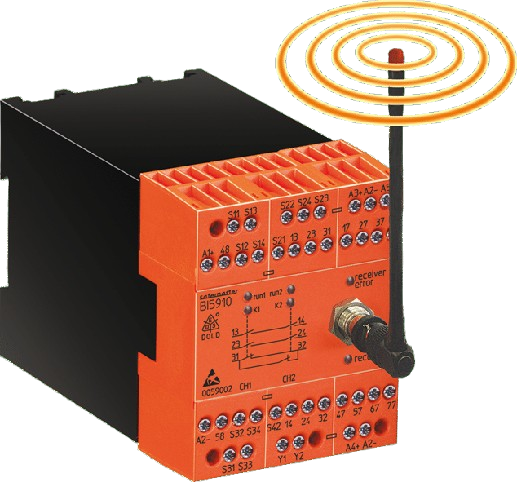
Wireless safety systems are advanced solutions designed to enhance machine and operator safety by using wireless communication to monitor, control, and respond to safety-related events…
Wireless safety systems are advanced solutions designed to enhance machine and operator safety by using wireless communication to monitor, control, and respond to safety-related events in industrial environments. These systems eliminate the need for traditional wired connections, providing increased flexibility, reduced installation time, and improved adaptability for dynamic and hard-to-reach areas. By integrating wireless technologies such as radio frequency (RF), Bluetooth, and proprietary communication protocols, wireless safety solutions enable real-time monitoring and rapid emergency response while maintaining compliance with strict safety regulations.
Key Features of Wireless Safety Systems:
- Wireless Emergency Stops: Handheld or stationary emergency stop buttons that communicate wirelessly to halt operations immediately during emergencies.
- Remote Monitoring: Allows safety status tracking and diagnostics from a distance, enabling proactive maintenance and faster issue resolution.
- Robust Wireless Protocols: Ensures secure and reliable communication with minimal latency and resistance to interference.
- Flexible Installation: Ideal for applications where cable routing is impractical, such as large machinery, moving equipment, or outdoor operations.
- Energy-Efficient Design: Low power consumption for extended battery life in portable safety devices.
Common Components of Wireless Safety Systems:
- Wireless Safety Controllers: Central units that receive signals from wireless devices and trigger appropriate safety responses.
- Wireless Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Devices: Portable or mounted buttons for quickly stopping machinery from anywhere within range.
- Wireless Safety Sensors: Devices such as pressure mats, light curtains, or proximity sensors that transmit data wirelessly to the controller.
- Wireless Communication Modules: Devices that ensure seamless communication between the safety system components.
Typical Applications:
- Large-Scale Industrial Plants: Remote monitoring and emergency stops for expansive facilities.
- Mobile and Autonomous Machinery: Ensures safety in applications with automated guided vehicles (AGVs), cranes, and forklifts.
- Outdoor and Harsh Environments: Ideal for outdoor equipment and installations where traditional cabling is difficult or expensive.
- Dynamic Workspaces: Useful for production lines with frequent reconfiguration or mobile workstations.
Benefits of Wireless Safety Systems:
- Enhanced Flexibility: Supports the reconfiguration of safety zones and devices without rewiring.
- Improved Efficiency: Reduces installation time and costs by eliminating extensive cabling.
- Increased Safety Coverage: Enables operators to trigger safety functions from any location within the wireless range.
- Scalability: Easily expand the system by adding new wireless components as needed.
- Reliability: Advanced wireless protocols ensure secure communication with minimal signal loss or interference.
Compliance and Security:
Modern wireless safety systems comply with international safety standards such as ISO 13849, IEC 61508, and IEC 62061, ensuring functional safety and performance. They are equipped with encryption and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
Wireless safety systems provide a powerful combination of convenience, safety, and scalability, making them ideal for complex industrial environments where flexibility and reliable safety controls are essential.
For more information you can read about our blog post here.
If you are unsure about your application contact Venus now. We solve problems!